Fig. 3.
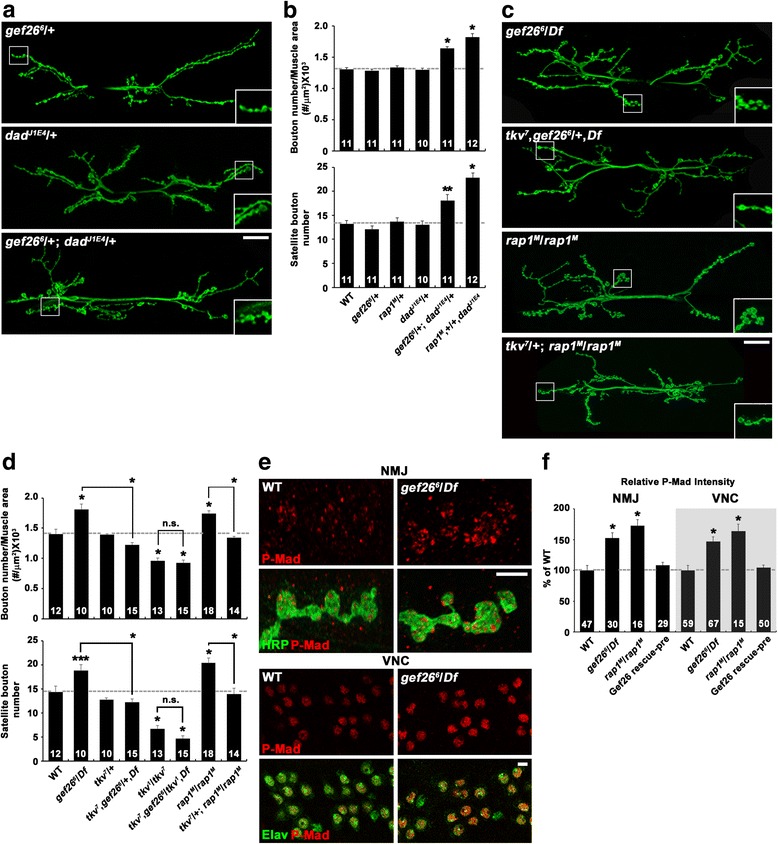
Gef26 and Rap1 inhibit BMP signaling to restrain synaptic growth. a-d gef26/rap1 interacts with BMP signaling pathway components. a and b Transheterozygous interactions between gef26 or rap1 and dad. a Confocal images of anti-HRP-labeled NMJ 6/7 in gef26 6/+, dad J1E4/+, and gef26 6/+; dad J1E4/+ third-instar larvae. Scale bar, 20 μm. b Quantification of total bouton number and satellite bouton number at NMJ 6/7 in the following genotypes: wild-type, gef26 6/+, rap1 M/+, dad J1E4/+, gef26 6/+; dad J1E4/+, and rap1 M, +/+,dadJ1E4. c and d Synaptic overgrowth in gef26 and rap1 depends on BMP signaling. c Confocal images of anti-HRP-labeled NMJ 6/7 in gef26 6/Df, tkv 7,gef26 6/+,Df, rap1 M/rap1 M, and tkv 7/+; rap1 M/rap1 M third-instar larvae. Scale bar, 20 μm. d Quantification of total bouton number and satellite bouton number at NMJ 6/7 in the following genotypes: wild-type, gef26 6/Df, tkv 7/+, tkv 7,gef26 6/+,Df, tkv 1/tkv 7, tkv 7,gef26 6/tkv 1,Df, rap1 M/rap1 M, and tkv 7/+; rap1 M/rap1 M. Note that synaptic overgrowth in gef26 and rap1 mutants is significantly suppressed by loss of one copy of tkv. e and f Levels of pMad are increased in gef26 and rap1 mutants. e Confocal images of NMJ 6/7 and ventral nerve cord (VNC) labeled with anti-P-Mad and anti-HRP or anti-Elav in wild-type and gef26 6/Df third-instar larvae. Scale bars, 5 μm. f Quantification of the ratio of the average levels of P-Mad to HRP or Elav. Genotypes include wild-type, gef26 6/Df, rap1 M/rap1 M, and C155-GAL4/+; gef26 6/Df; UAS-gef26/+ (Gef26 rescue-pre). The number of NMJs or VNCs analyzed is indicated in each bar. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. All comparisons are made with wild-type unless otherwise indicated (*P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.05; n.s., not significant)
