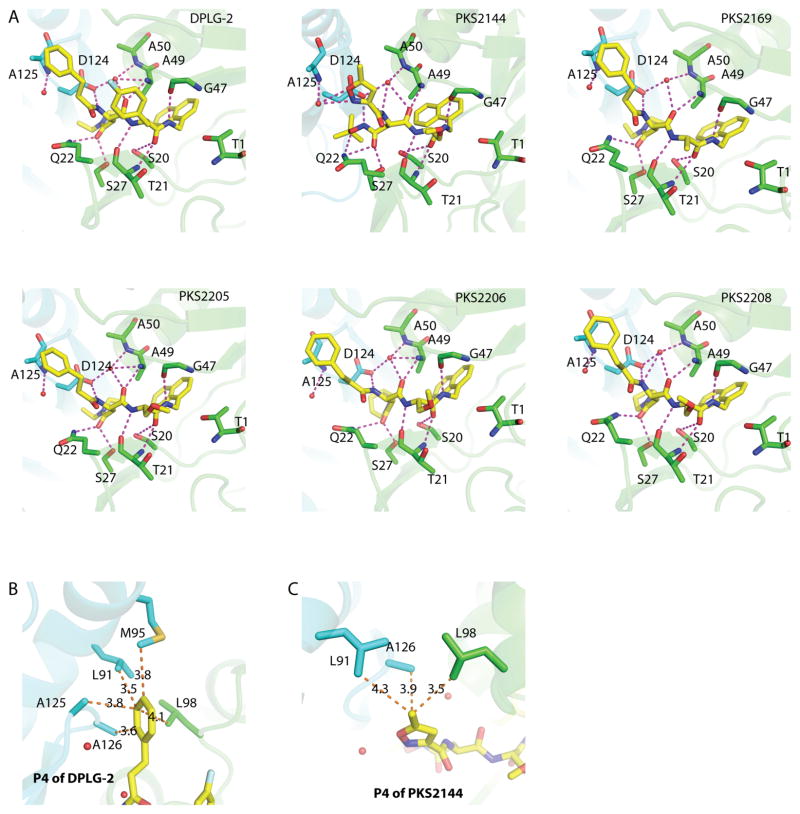
Figure 4. The binding mode of the dipeptides in Mtb20SOG.
(A) In addition to the antiparallel bindings between the inhibitor backbone and Thr-21, Gly-47, and Ala-49, also within hydrogen-bonding distance are the surrounding amino acids, including Ser-20, Gln-22, Ser-27, Ala-50, and Asp-124 of neighboring subunits, and a water molecule. Possible hydrogen bonds between the inhibitors and the proteasome are shown as magenta dashed lines; the two neighboring β-subunits are shown in green and cyan; water molecules are shown as red spheres. PKS2144 has extra hydrogen-bonding capacities between tBu-O-NH of the P3-Asn side chain and Asp-124, between tBu-O-NH of the P3-Asn side chain and Gln-22, and between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms of the 5-methylisoxazole of P4 and Ala-125 through a water molecule. (B) The five dipeptides that contain a phenylpropanoyl P4 group can form additional hydrophobic interactions with Leu-98, and with Leu-91, Met-95, Ala-125, and Ala-126 of neighboring subunits. Pictured is DPLG-2; the distances between the P4 3-phenylpropanoyl group and the surrounding amino acids are shown as orange dashed lines. (C) PKS2144 has a 5-methylisoxazole group at the P4 position, which forms hydrophobic interactions with the surrounding amino acids. H-bond interactions are shown in panel A.