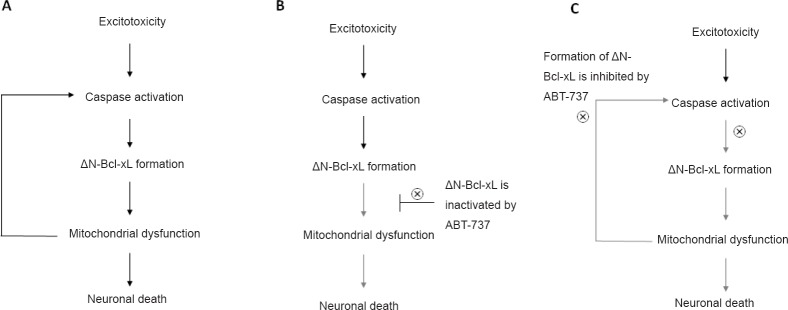
Figure 1.
ABT-737 inhibits activity and formation of ΔN-Bcl-xL.
(A) Excitotoxic stimulation caused by cerebral ischemia triggers caspase-dependent cleavage of Bcl-xL and forms ΔN-Bcl-xL. Accumulation of ΔN-Bcl-xL at the inner membrane leads to mitochondrial dysfunction associated with mPTP opening and cytocrome c release, then eventually causes neuronal death. (B) Excitotoxic stimulation produces ΔN-Bcl-xL protein, but ABT-737 binds with the active site of ΔN-Bcl-xL, therefore inactivates neurotoxic functions of ΔN-Bcl-xL at the mitochondria (the immediate mechanism of action of ABT-737). (C) Inactivation of ΔN-Bcl-xL by ABT-737 blocks mPTP opening and cytocrome c release which eventually inhibits caspase activation (delayed function of ABT-737). Therefore, application of ABT-737 also blocks formation of ΔN-Bcl-xL. Bcl-xL: B-cell lymphoma-extra large; mPTP: mitochondrial permeablity transition pore.