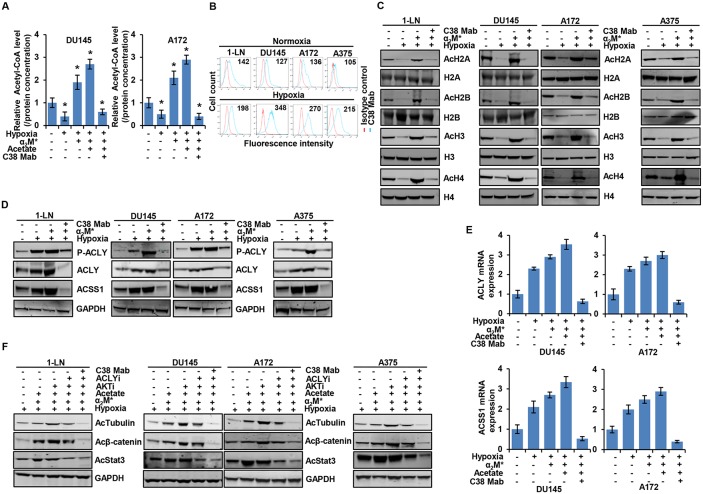
Figure 5. α2M*/CS-GRP78 rescues hypoxia-induced reduction of histone acetylation.
(A) The total cellular concentration of acetyl-CoA was measured in the indicated cell lines under normoxia and hypoxia conditions. The cells were treated with C38 Mab (50 μg) for 6 h and then stimulated with α2M* (100 pM) for 30 min and acetate (5 mM) for 4 h. mean ± SEM of triplicates. (B) Surface expression of GRP78 was detected in the indicated cancer cell lines under normoxia or hypoxia by flow cytometric analysis of nonpermeabilized cells. Surface GRP78 was visualized with murine monoclonal antibody C38, followed by fluorescently labeled secondary antibody and the relative to matched isotype control. Positively stained cells are represented as the area under the respective histogram, and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values are shown. (C-D) Immunoblot analysis of the indicated cancer cell lines under normoxia or hypoxia treated with C38 Mab (50 μg) for 6 h and then stimulated with α2M* (100 pM) for 30 min. (E) Indicated cancer cell lines under normoxia or hypoxia were treated with C38 Mab (50 μg) for 6 h and then stimulated with α2M* (100 pM) for 30 min and acetate (5 mM) for 4 h to quantify the transcript level of ACLY and ACSS1 genes. (F) Immunoblot analysis of protein acetylation levels in indicated cancer cell lines under normoxia or hypoxia stimulated either alone or in combination with α2M* (100 pM) for 30 min or acetate (5 mM) for 4 h in the absence and presence of ACLYi (100 μM) for 16 h, AKTi (GSK690693, 5 μM/L) for 16 h or C38 Mab (50 μg) for 6 h. *, p values ≤ 0.05. Error bar represent S.D.