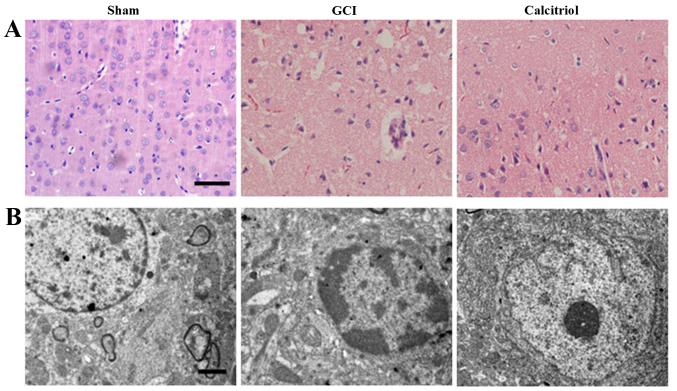
Figure 2.
Morphological detection results in the cortex region of the brain after GCI. (A) Assessment of histopathologic changes in the experimental groups (hematoxylin and eosin staining; scale bar, 50 μm). The nuclei of normal neurons were round and stained pale, whereas nuclei of dying neurons were pyknotic and darkly stained after GCI. The pathological changes of cortex neurons in the calcitriol-treated group were improved compared with those in the GCI group. (B) Ultrastructures of neurons were observed via transmission electron microscopy in the experimental groups (scale bar, 2 μm). In the Sham group, the neurons in the cortex had large round nuclei, the double nuclear membranes were clear and complete, and the outer membrane enclosed the periphery of the mitochondria. In the GCI group, neurons were irregular and exhibited chromatin condensation, cytoplasm dissolution and vacuole formation. The nuclear membranes and cell organelles were dissolved or absent. In the calcitriol group, the damage to the neurons was alleviated. GCI, global cerebral ischemia.