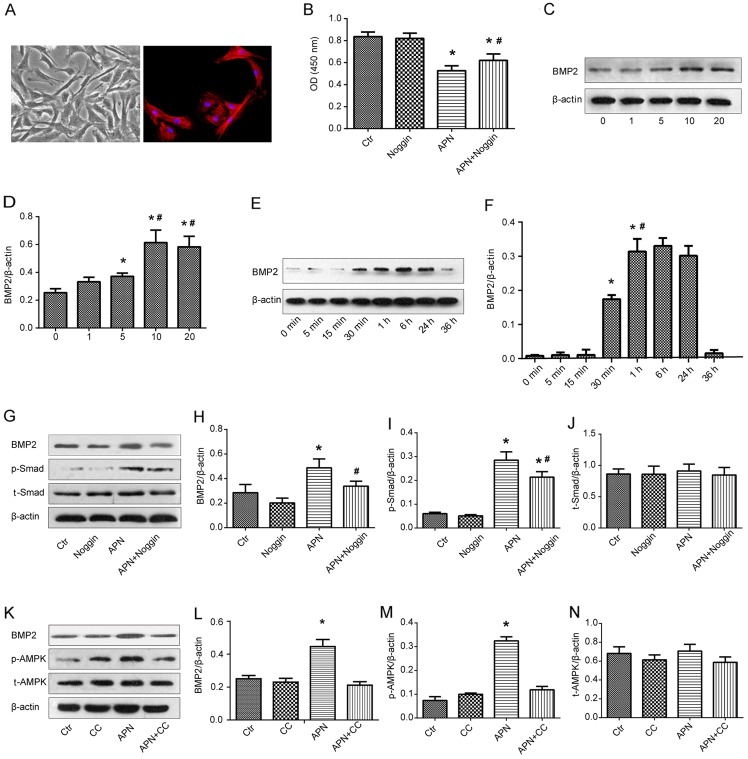
Figure 4.
Effect of adiponectin (APN) on pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). (A) Left, typical 'hill and valley' appearance of rat PASMCs under phase contrast microscope; right, positive immunofluorescent identification of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA). (B) Cell proliferation was analyzed by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. (C and D) PASMCs were incubated with APN (0–20 μg/ml) for 1 h and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP2) expression was measured by western blot analysis. *P<0.05 vs. 0 μg/ml group; #P<0.05 vs. 5 μg/ml group. (E and F) PASMCs were incubated with 10 μg/ml APN for indicated time intervals and BMP2 expression was measured by western blot analysis. *P<0.05 vs. 0 min group; #P<0.05 vs. 30 min group. (G–N) Adiponectin (APN) exerted antiproliferative effects by modulating the AMPK/BMP/Smad signaling pathway. (G–J) Rat PASMCs were exposed to APN (10 μg/ml) and/or noggin (200 ng/ml) and BMP2, p-Smad and Smad expression was analyzed with western blot analysis. (K–N) PASMCs were treated with compound C (20 μmol/l) and/or APN (10 μg/ml) and BMP2, p-AMPK and AMPK expression was analyzed by western blot analysis. CC, Compound C. *P<0.05 vs. Ctr group; #P<0.05 vs. APN group.