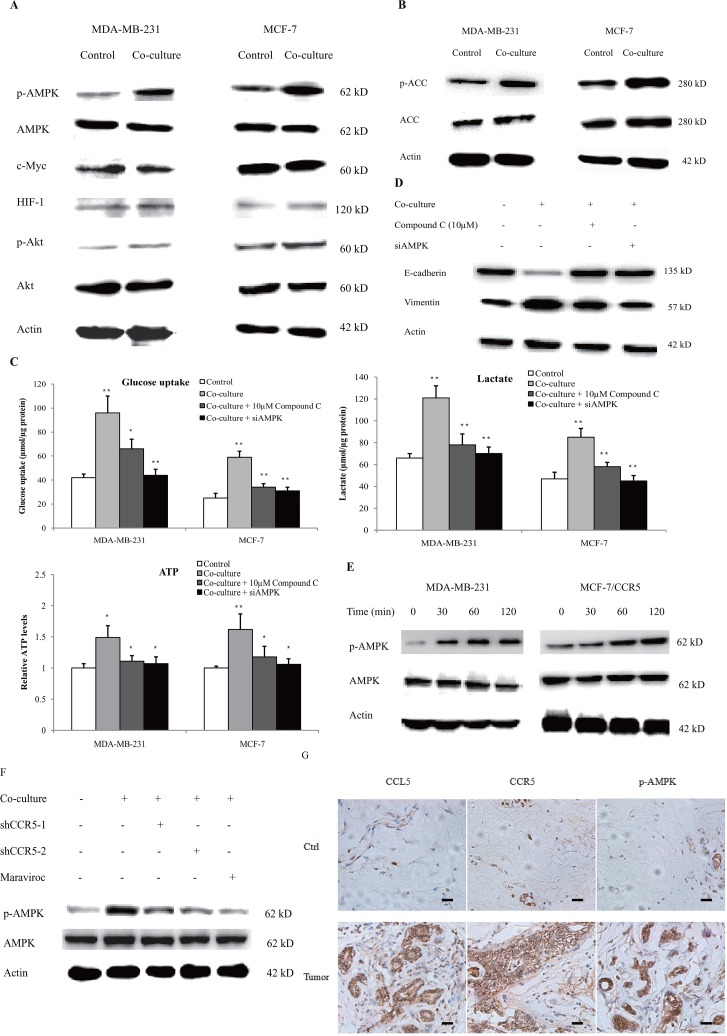
Figure 7. CCL5-CCR5 axis induced aerobic glycolysis by regulation of AMPK signaling.
(A) Western blot for AMPK, c-Myc, HIF-1α and Akt in breast cancer cells co-cultured with 15mM lactic acid-activated THP-1 macrophages (ratio 1:1) for 72 h. Results presented were representatives of at least three independent experiments. (B) The expression of AMPK downstream signaling target ACC in breast cancer cells co-cultured as in (A). (C) MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells were transfected with 50 nM AMPKα1 siRNA, or pretreated with 10μM compound C for 4 h, and then incubated with 15mM lactic acid-activated THP-1 macrophages (ratio 1:1) for 48 h. The glucose uptake, lactic acid production and ATP levels were detected. (D) The inhibition of AMPK abrogated macrophage-induced EMT in MCF-7 cells. Cells were treated as described in (C). After co-culture, the expression of EMT markers, E-cadherin and vimentin, was measured by western blot. (E) Recombinant human CCL5 induced the phosphorylation of AMPK in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7/CCR5 cells. 106 cells were treated with 50ng/ml CCL5 for defferent time points as indicated, and phosphorylated AMPK and total AMPK were investigated by western blot. (F) Inhibition of CCR5 in MDA-MB-231 cells significantly attenuated macrophage-induced AMPK phosphorylation. MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with shRNAs designed against CCR5, or pre-treated with 5μM Maraviroc for 2 h, then co-cultured with 15 mM lactate-activated macrophages as described in (A). After co-culture, the phosphorylation of AMPK was detected by western blot. (G) Expressions of CCL5, CCR5 and p-AMPK in samples obtained from breast cancer patients (n =28). Scale bars represent 50 μm. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.