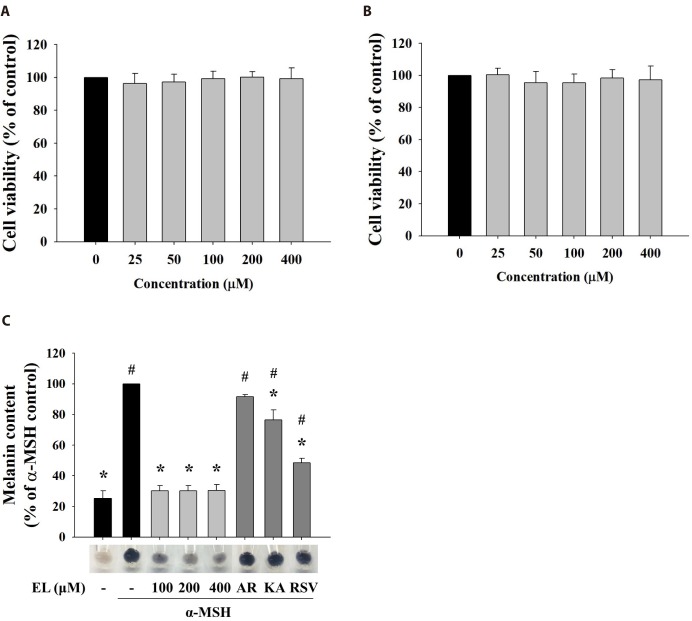
Fig. 1. Effects of cell cytotoxicity and melanin production of ethyl linoleate.
The cells were treated for 48 h with indicated concentration of ethyl linoleate. Cell viabilities were determined by MTT assay on B16F10 murine melanoma (A) and human dermal fibroblast cells (B). (C) The B16F10 cells were exposed to α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH, 500 nM) in the presence of ethyl linoleate (EL) for 48 h. Melanin content in B16F10 cells was visualized and determined at the indicated concentrations of EL or positive whitening agents (AR, arbutin 2 mM; KA, kojic acid 400 µM; RSV, resveratrol 20 µM). The data are expressed as the means±SD. *p<0.01, compared with the α-MSH control; #p<0.01, compared with the vehicle control.