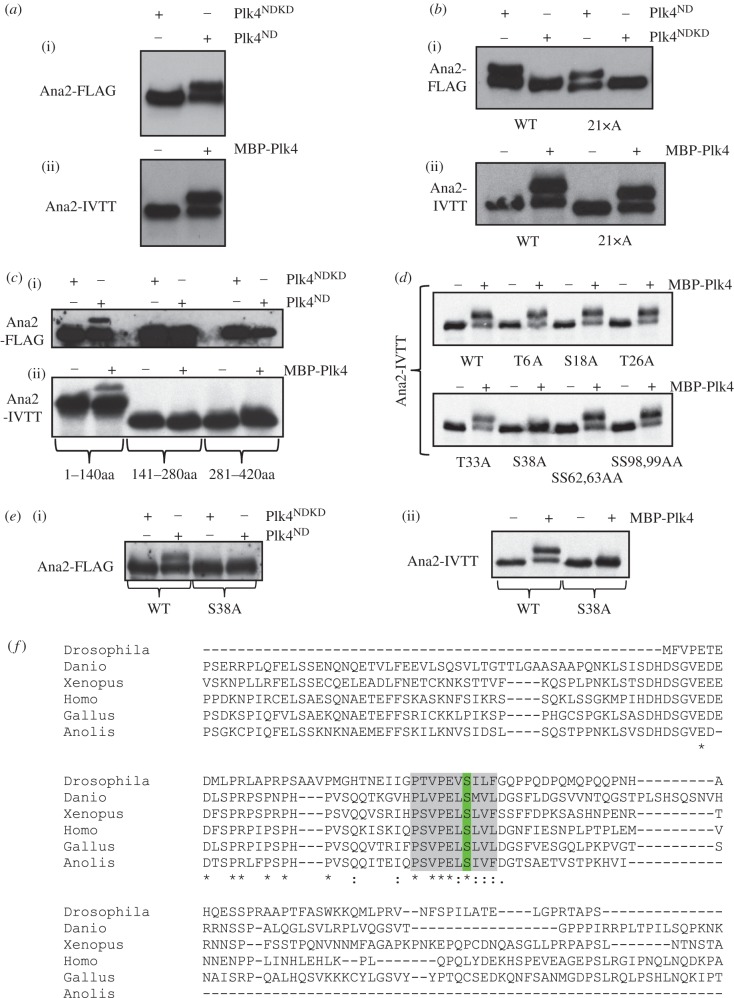
Figure 5.
Plk4 phosphorylates Ana2 at conserved serine 38. (a) (i) Transient co-overexpression of Ana2-FLAG with active or kinase-dead non-degradable Plk4 (Plk4ND or Plk4NDKD respectively) in D.Mel-2 cells. Cell extracts were subjected to western blotting to reveal the Ana2-FLAG protein. (ii) 35S-Met-Ana2 protein synthesized by coupled transcription–translation in vitro and incubated with MBP-Plk4 and ATP in vitro and analysed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Plk4-mediated phosphorylation in vivo or in vitro results in a shift in the electrophoretic mobility of Ana2. (b) Phosphorylation of Ana2 in which all 21 in vitro phosphorylation sites (highlighted in blue in electronic supplementary material, figure S1D) have been mutated to alanine residues. Assays are carried out using either the in vivo co-overexpression assay (i) or the in vitro phosphorylation assay (ii). None of the 21 mutations abolishes the band-shift. (c) The phosphorylation site responsible for the band shift is located within the N-terminal 140 amino acids of Ana2. Of the three Ana2 fragments, Ana21–140, Ana2141–280 and Ana2281–420, only Ana21–140 displays the band-shift in both the co-overexpression (i) and the in vitro phosphorylation assay (ii). (d) An S38A-Ana2 mutation, but not mutations in other candidate sites in the N-terminal 140 amino acids, abolishes the band-shift resulting from incubation with Plk4 in vitro. (e) The S38A mutation abolishes the shift in electrophoretic mobility of Ana2 following phosphorylation by Plk4 in either the in vivo co-overexpression assay (i) or in the in vitro assay (ii). (f) S38 (green) lies within a conserved region of Ana2—the ANST motif (highlighted grey). Partial alignment of Drosophila melanogaster Ana2 (top line) with STIL orthologues from Danio rerio, Xenopus laevis, Homo sapiens, Gallus gallus and Anolis carolinensis.