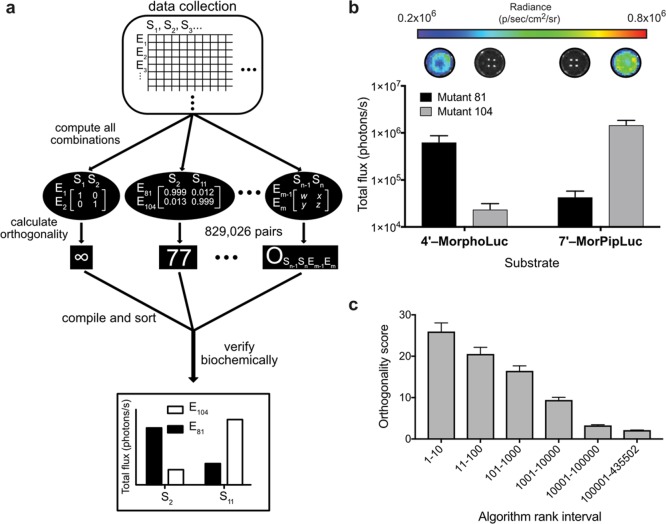
Figure 2.
Uncovering orthogonal pairs in silico. (a) Computational approach to identifying orthogonal sets. Parallel screens of mutant enzymes (Em) and substrate analogues (Sn, where n and m are integers) were performed and light emission values entered into a database. Data were analyzed with a custom computer script to identify orthogonal sets. (b) Sample orthogonal bioluminescent probes. Bacteria expressing mutant enzymes were expanded, lysed, and distributed evenly among replicate wells. Lysates were treated with luciferin analogues and imaged. Representative images are shown, along with quantified photon outputs. (c) Orthogonality scores correlated with computer script rank. Orthogonal sets predicted in silico were verified biochemically as in panel b. Each bar (beyond rank 11) represents >40 unique sets that were evaluated in head-to-head comparisons in vitro. (For interval 1-10, all ten orthogonal sets were examined). For panels b and c, error bars represent the standard error of the mean for n ≥ 3 experiments.