Figure 3. S-adenosylmethionine binds SAMTOR to disrupt its interaction with GATOR1 and KICSTOR.
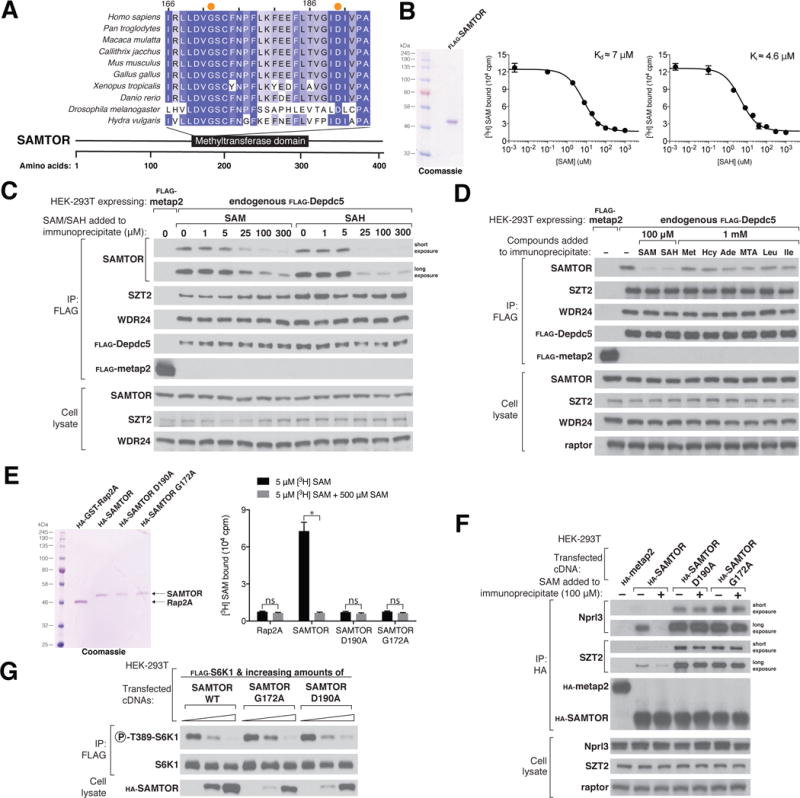
(A) Schematic of the human SAMTOR protein indicating the class I Rossmann fold methyltransferase domain. Shown is an alignment of partial sequences of this domain from SAMTOR in indicated species. Amino acid positions are colored from white to blue in order of increasing sequence similarity. Orange dots denote the Gly172 and Asp190 residues of human SAMTOR.
(B) SAMTOR binds SAM and SAH. Purified FLAG-SAMTOR protein was analyzed by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by Coomassie blue staining. Binding assays were performed with purified FLAG-SAMTOR incubated with the indicated concentrations of [3H]SAM, unlabeled SAM, or SAH.Values for each point are means ± SD of three technical replicates fromone representative experiment. The experiment was performed twice.
(C) SAM and SAH disrupt the interaction of SAMTOR with GATOR1 in vitro. FLAG immunoprecipitates were prepared from endogenously FLAG-tagged Depdc5 HEK-293Tcells. SAM and SAH were added directly to the immunoprecipitates at the indicated concentrations. FLAG immunoprecipitates and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for the levels of the indicated proteins.
(D) The interaction between SAMTOR and GATOR1 is disrupted by 100 μM SAM or SAH, but not by 1mM methionine, homocysteine, adenosine, 5-methylthioadenosine, leucine, or isoleucine. The experiment was performed and analyzed as in (C).
(E) Wild-type HA-SAMTOR, but not HA-SAMTOR G172A or D190A, binds SAM. HA-tagged wild-type and mutant SAMTOR proteins were prepared from HEK-293Tcells expressing the indicated cDNAs, and binding assays were performed as in (B). A representative experiment is shown; values are means ± SD of three technical replicates.Two-tailed t tests were used for comparisons between two groups. *P < 0.001; ns, not significant. The experiment was repeated three times.
(F) HA-SAMTOR G172A and D190A coimmunoprecipitate more endogenous GATOR1 and KICSTOR than does wild-type SAMTOR, and the interactions are insensitive to SAM added in vitro. HA immunoprecipitates and cell lysates were prepared from HEK-293Tcells transiently expressing wild-type HA-SAMTOR or its mutants G172A or D190A. SAM was added to the immunoprecipitates where indicated. HA immunoprecipitates and cell lysates were analyzed as in (C).
(G) HA-SAMTOR G172A and D190A inhibit mTORC1 activity to similar extents as wild-type SAMTOR. FLAG immunoprecipitates were prepared from HEK-293Tcells transfected with the indicated cDNAs. FLAG immunoprecipitates and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for the phosphorylation states and levels of the indicated proteins.
