Figure 3. Inhibiting mitochondrial fission with Mdivi-1 reduces cocaine-induced D1-MSN adaptations.
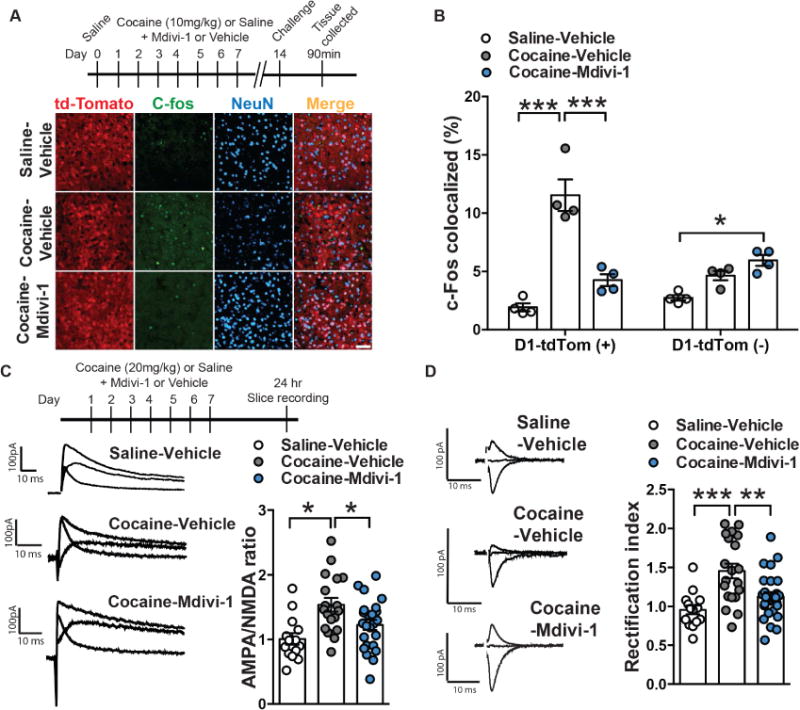
(A) Representative confocal images of D1-MSNs (red), c-Fos (green) and neuronal marker NeuN (blue) in Saline-Vehicle (top), Cocaine-Vehicle (middle) and Cocaine-Mdivi-1 (bottom) groups. Scale bar: 50μm. (B) Mdivi-1 (50mg/kg, ip) reduced cocaine-induced c-Fos colocalization in D1-MSNs and leads to a modest increase of c-Fos colocalization in non-D1-MSN cells when compared to saline-vehicle controls. Two-way ANOVA: Interaction: F(2,18)=25.41, p<0.0001, Tukey post-hoc: p<0.001 and p<0.05 respectively. n=4 in each group. (C) Representative traces of AMPA/NMDA ratio in D1-MSNs of mice pre-treated with vehicle and receiving saline, mice pre-treated with vehicle receiving cocaine and mice pre-treated with Mdivi-1 receiving cocaine (left panel). Mdivi-1 (50mk/kg, ip) normalized cocaine-induced increase in AMPA/NMDA ratio: One-way ANOVA: F(2,53)=7.214, p=0.0017, Tukey post-hoc: p<0.05. Saline-Vehicle: n=14 cells, Cocaine-Vehicle: n=18 cells and Cocaine-Mdivi-1: n=24 cells, all obtained from 6 mice in each group (right panel). (D) Representative traces of rectification index in saline-vehicle (top), cocaine-vehicle (middle) and cocaine-Mdivi-1 (bottom) pre-treated mice (left panel). Quantification of AMPA current rectification index (RI): cocaine increased the RI relative to saline-treated controls, while Mdivi-1 treatment (50mg/kg, ip) reduced the RI in cocaine treated mice: One-way ANOVA: F(2,58)=11.01, p<0.0001, Tukey post-hoc: p<0.001 and p<0.01; Saline-Vehicle: n=15 cells, Cocaine-Vehicle: n=20 cells and Cocaine-Mdivi-1: n=26 cells, all obtained from 6 mice in each group (right panel). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Error bars, SEM. See also Figure S3.
