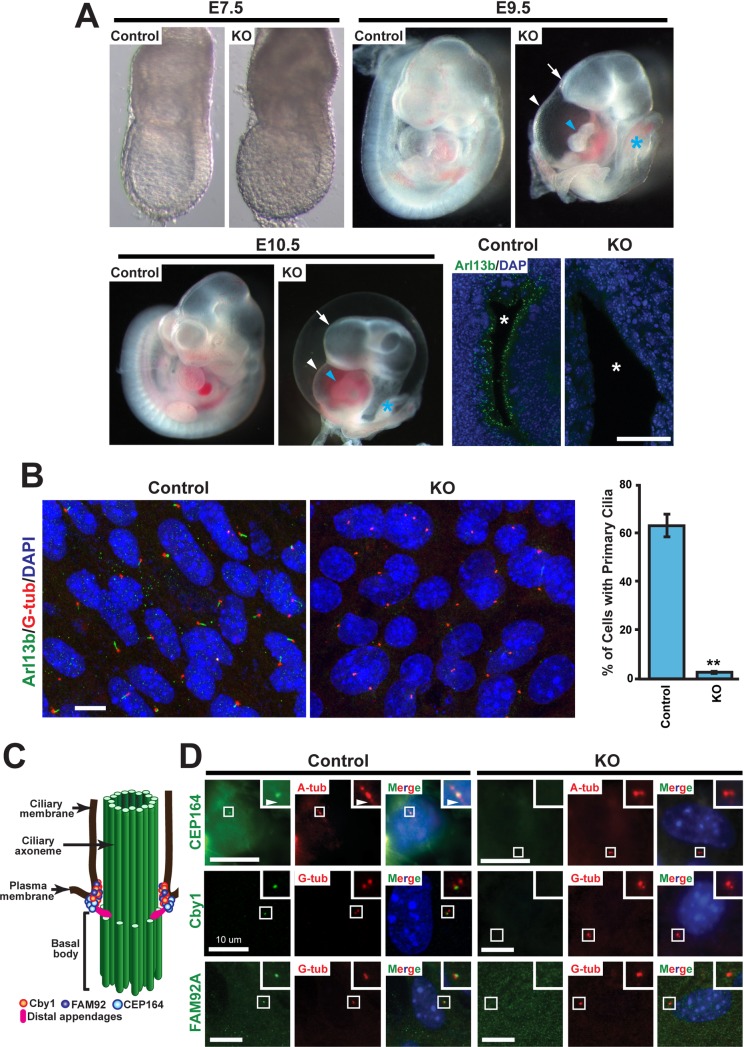
Fig 1. CEP164 is essential for early embryonic development and primary ciliogenesis.
(A) Comparison of control (WT or heterozygous) embryos with CEP164-knockout (KO) littermates at E7.5, E9.5, and E10.5. At E7.5, KO embryos were indistinguishable from control littermates. In contrast, E9.5 and E10.5 KO embryos displayed holoprosencephaly (arrow), an edematous pericardial sac (white arrowhead), cardiac looping defects (blue arrowhead), and a truncated posterior trunk (blue asterisk). Confocal images of neural tube sections from E9.5 control and KO embryos are presented in lower right panels. Primary cilia were labeled with the ciliary marker Arl13b (green), and nuclei are visualized with DAPI staining (blue). Asterisks indicate the lumen of the neural tube. Scale bar, 35 μm. (B) Loss of primary cilia in CEP164-KO MEFs. Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were prepared from E8.5 CEP164-KO or control embryos, serum-starved for 48 hours to induce primary cilia, and immunostained for Arl13b (green) and the basal body marker γ-tubulin (G-tub) (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. Quantification is shown on the right. >200 cells were counted for each of three independent MEF preparations per genotype. Error bars represent ±SEM. **, p<0.01. (C) Schematic depiction of the localization of Cby1, FAM92, and CEP164 at the ciliary base. Basal bodies and centrioles are barrel-shaped structures composed of nine microtubule triplets. During ciliogenesis, mother centrioles transform into basal bodies by acquiring accessary structures to assemble cilia. The axoneme is the detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal structure of the cilium including microtubules and their associated proteins. (D) Serum-starved MEFs were double-labeled for CEP164, Cby1, or FAM92A (green) and the ciliary marker acetylated α-tubulin (A-tub) or G-tub (red) as indicated. Nuclei were visualized by DAPI (blue). The boxed regions are enlarged in insets, highlighting the loss of CEP164, Cby1, and FAM92A centriolar localization in CEP164-KO MEFs. Arrowheads point to primary cilia. Scale bars, 10 μm.