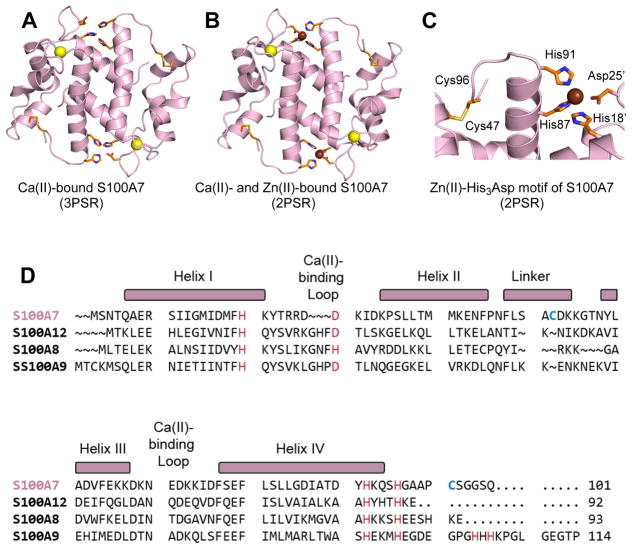
Figure 1.
Crystal structures of human S100A7 and amino acid sequence alignment of S100A7 and select human S100 polypeptides. (A) Structure of the Ca(II)-bound S100A7 homodimer (PDB 3PSR).6 (B) Structure of the Ca(II)- and Zn(II)-bound S100A7 homodimer (PDB 2PSR).6 (C) Zoom-in view showing the His3Asp motif and Cys47–Cys96 disulfide. Ca(II) ions are shown as yellow spheres, and Zn(II) ions as brown spheres. (D) Sequence alignment of human S100A7, human S100A8, human S100A9, and human S100A12. The secondary structural elements presented above the alignment are for human S100A7. The transition-metal binding residues are presented in red and Cys47 and Cys96 of S100A7 are highlighted in blue.