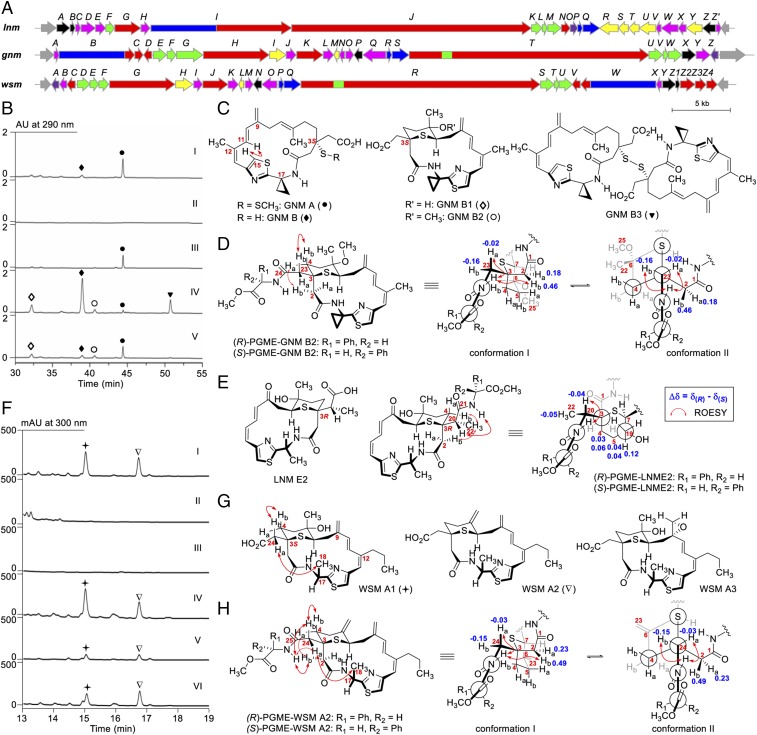
Fig. 4.
Discovery of GNMs and WSMs exemplifying the rich structural diversity of the LNM family of natural products. (A) Genetic organizations of the gnm and wsm gene clusters in comparison with the lnm gene cluster. (B) HPLC analysis of fermentations of the S. sp. CB01883 wild-type (I), SB21001 (i.e., ΔgnmB) (II), SB21002 (i.e., ΔgnmB/pBS21005) (III), SB21003 (i.e., ΔgnmO) (IV), and SB21004 (i.e., ΔgnmO/pBS21007) (V) mutant strains. (C) Structures of GNMs isolated from the S. sp. CB01883 wild-type (GNM A and B) and SB21003 mutant (GNM B, B1, B2, and B3). (D) Determination of the absolute configuration of GNMs at C3 to be S as shown based on the differences of the chemical shifts in 1H NMR of H2 and H23 between (R)- and (S)-PGME derivatives of GNM B2. Two major conformations are shown based on the analysis of their ROESY correlation signals (see SI Appendix, Fig. S14 for details). (E) Confirmation of the absolute configuration of LNM E2 at C3 to be R as shown based on the differences of the chemical shifts in 1H NMR of H4, H5, and H22 between the (R)- and (S)-PGME derivatives of LNM E2 (see SI Appendix, Fig. S16 for details). (F) HPLC analysis of fermentations of the S. sp. CB02120-2 wild-type (I), SB22001 (i.e., ΔwsmW) (II), SB22002 (i.e., ΔwsmZ3) (III), SB22003 (i.e., ΔwsmZ3/pBS22006) (IV), SB22004 (i.e., ΔwsmZ4) (V), and SB22005 (i.e., ΔwsmZ4/pBS22008) (VI) mutant strains. (G) Structures of WSMs isolated from the S. sp. CB02120-2 wild-type strain. (H) Determination of the absolute configuration of WSMs at C3 to be S as shown based on the differences of the chemical shifts in 1H NMR of H2 and H24 between (R)- and (S)-PGME derivatives of WSM A2 (see SI Appendix, Fig. S24 for details). Ha and Hb denote one of the two geminal hydrogens appearing at lower and higher field, respectively, in 1H NMR. GNM A, ●; GNM B, ◆; GNM B1, ◇; GNM B2, ○; GNM B3, ▼; WSM A1, ✦; WSM A2, ∇.