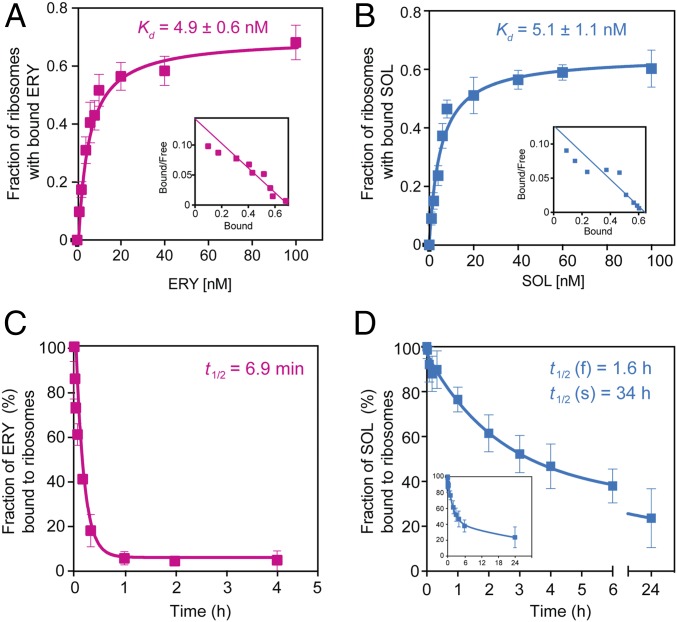
Fig. 3.
Thermodynamic and kinetic parameters of interaction of bacteriostatic and bactericidal macrolides with the bacterial ribosome. (A and B) Equilibrium binding of [14C]-ERY (A) or [14C]-SOL (B) to S. pneumoniae ribosomes. Ribosomes were mixed with varying concentrations of the radiolabeled drugs and incubated for 2 h at 37 °C before determining the amount of bound antibiotic (see Materials and Methods for details). Insets show the Scatchard plots for ERY and SOL equilibrium binding. (C and D) Kinetics of dissociation of [14C]-ERY (C) or [14C]-SOL (D) from the ribosome. The Inset in D shows the complete curve. Ribosomes were preequilibrated with the [14C]-labeled antibiotics and after addition of an excess of the respective nonlabeled drug the amount of ribosome-associated radioactivity was monitored over time. The data were fitted to a one-phase (ERY) or two-phase (SOL) exponential functions that yielded dissociation rate constants of (10 ± 1.4) × 10−2 min−1 for ERY, (0.72 ± 0.25) × 10−2 min−1 for the faster (f) phase of SOL, and (0.034 ± 0.02) × 10−2 min−1 for the slower (s) phase of SOL. The values of dissociation rate constants were used for calculating the half-life (t1/2) of the complexes (shown in the figure). All experiments were performed in triplicates. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD).