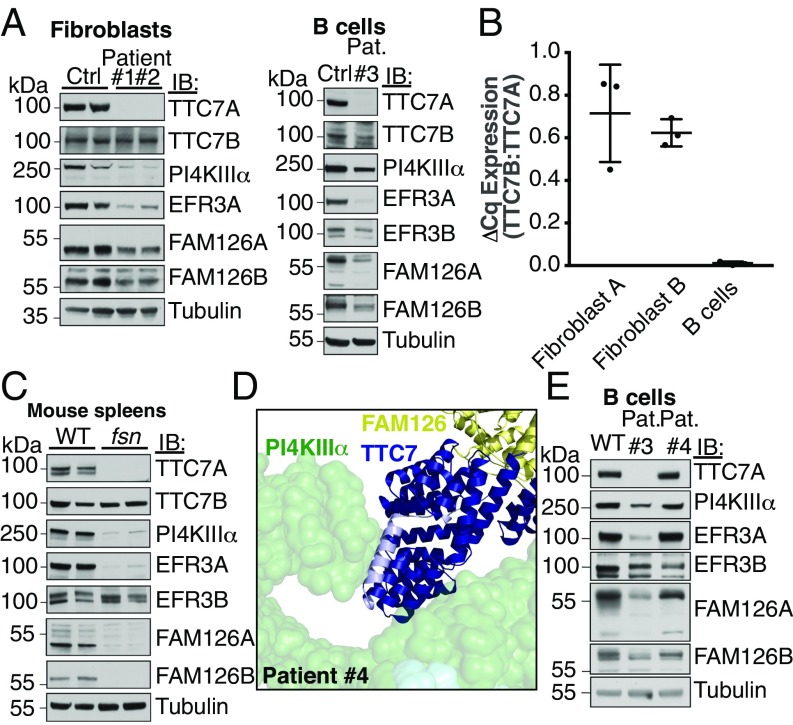
Fig. 3.
The interaction between TTC7 and PI4KIIIα is required for PI4KIIIα stability in vivo. (A) Patient fibroblasts or B cells were isolated and immunoblotted with antibodies against components of the PI4KIIIα complex. The levels of other complex subunits are reduced in the absence of intact TTC7A. (B) TTC7B mRNA is less abundant than TTC7A mRNA in human fibroblasts and nearly absent in B cells. cDNA from control human fibroblasts and B cells used in C was analyzed by qRT-PCR with TTC7A- and TTC7B-specific primer pairs. The ratio of TTC7B expression to that of TTC7A is shown for each cell type. Error bars represent SD (n = 3). (C) Spleens isolated from “flaky skin” mice (17, 18) were immunoblotted for PI4KA complex subunits. Loss of TTC7A caused reduction in the levels of other complex components. (D) CID-MIA patient 4 carries a mutation that truncates TTC7A at residue 823 (corresponding to residue 809 of TTC7B). The corresponding truncated residues are indicated in light blue on the structure of TTC7B in the context of the kinase complex. This mutation likely abolishes the interaction between TTC7 and the tip of the PI4KIIIα α-solenoid, causing the pathology of CID-MIA. (E) CID-MIA patient 4 carries an intact, though mildly truncated version of TTC7A. Immunoblots for other PI4KA complex components indicate little change in protein levels. Immunoblots against B cells from patient 3 are shown for comparison. Ctrl, Control; IB, immunoblot; Pat., Patient.