Figure 1.
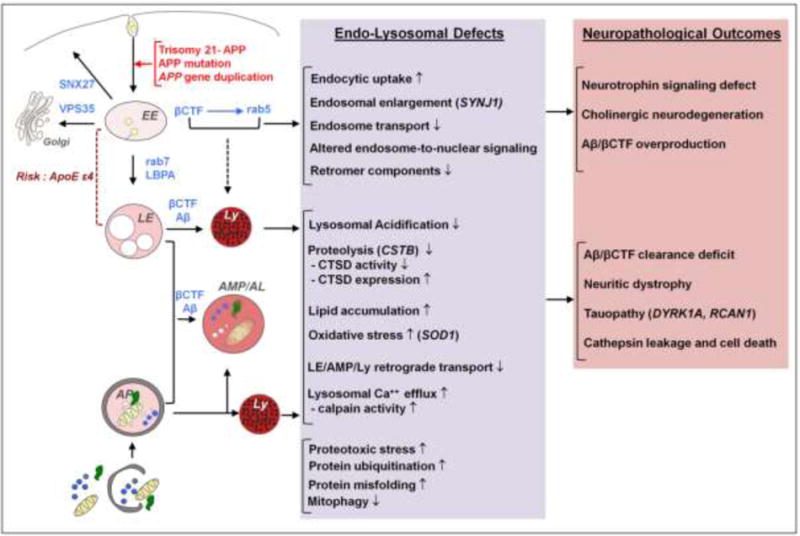
Overview of the shared pathways and pathological mechanisms driven by the APP gene and its cleavage products (βCTF/Aβ) in DS and AD: known and predicted endocytic and lysosomal factors contributing to neurodegeneration. Genetic contributors to neurodegeneration in DS other than APP are shown in parentheses. ApoE ε4, a known genetic risk factor for AD, contributes to endolysosomal dysfunction in AD and potentially in DS. EE, early endosome; LE, late endosome; AP, autophagosome; Ly, Lysosome; AMP/AL, amphisome/autolysosome.
