Figure 3.
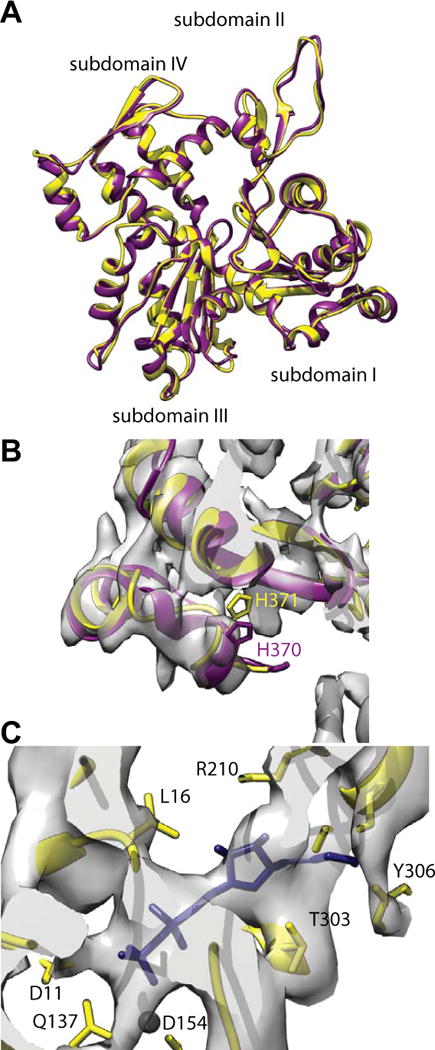
Comparison of vertebrate non-muscle γ-actin and skeletal muscle α-actin subunits. (A) Overlay of the fitted actin subunits. Skeletal muscle α-actin is colored yellow and the non-muscle γ-actin subunit colored dark magenta. (B) Region near the C-terminus. The rabbit α-actin subunit used for initiating the fitting did not include four residues at the C-terminus. These were added in later but have not been energy minimized. The C-termini of the non-muscle γ-actin subunit fits the density very well indicating that after refinement, the muscle α-actin C-terminus will likely be very similar. (C) Region near the ADP binding site. Substantial density is present where the nucleotide binds. The black sphere is a magnesium ion for which clear density is not visible. Its presence provides a useful landmark.
