Figure 1. Mechanisms of lncRNA action.
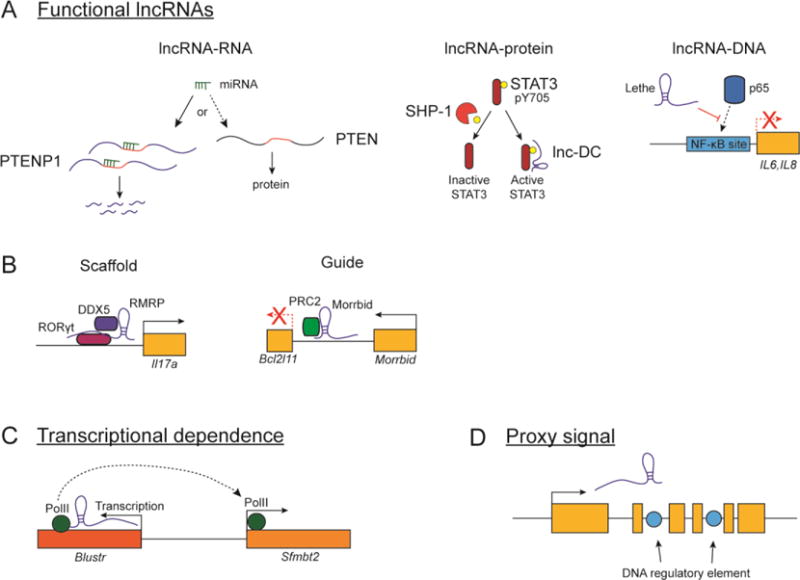
(A) lncRNA mechanisms that depend on the RNA molecule itself include lncRNA-RNA, lncRNA-protein, and lncRNA-DNA-based mechanisms. For example, PTENP1 encodes miRNA target sequences shared by PTEN and acts as a “sponge” for miRNAs targeting PTEN (left). lnc-DC interacts directly with the protein STAT3 and blocks its dephosphorylation by the phosphatase SHP-1 (middle). lncRNA Lethe hinders the recruitment of NF-κB p65 subunit to its target DNA sequences (right).
(B) lncRNAs can activate gene expression by acting as scaffolds for interactions between other proteins, such as lncRNA RMRP (left), or as guides to direct the recruitment of chromatin modifying complexes to neighboring genes, such as Morrbid (right).
(C) The act of lncRNA transcription can intrinsically account for the activity of some lncRNA loci. Transcription across the lncRNA Blustr directly promotes transcription of its neighboring gene Sfmbt2.
(D) Some lncRNAs may not regulate transcription of their target genes, but instead act as a proxy signals for important DNA regulatory elements embedded within the lncRNA locus.
