Figure 3. lncRNAs in the adaptive immune system.
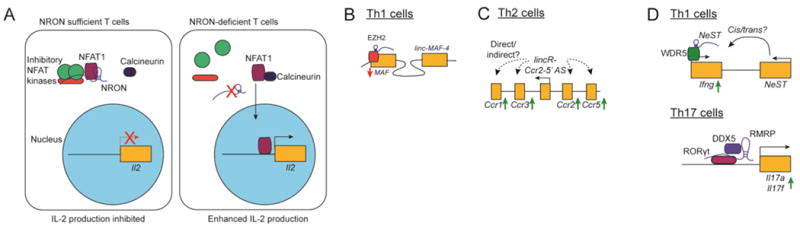
(A) The lncRNA NRON represses T cell NFAT1 activity by promoting its association with inhibitory factors in the cytoplasm. In the absence of NRON, the phosphatase Calcineurin is able to dephosphorylate NFAT1, resulting in its nuclear translocation and increased cytokine production.
(B) lncRNAs promote Th1 cell polarization. linc-MAF-4 promotes the recruitment of EZH2 to the promoter of the Th2-specific transcription factor c-MAF to repress its expression.
(C) LincR-Ccr2-5′AS promotes expression of Th2 genes, including nearby chemokine receptors such as Ccr1, Ccr2, Ccr3, and Ccr5. Whether this regulation is direct or indirect, and the specific mechanisms through which LincR-Ccr2-5′AS regulate these genes is unknown.
(D) lncRNAs promote T cell effector function. NeST promotes WDR5 recruitment to the Ifng locus to activate its transcription (above), while RMRP promotes Th17 cytokine production by acting as a scaffold for the association of the Th17-specific transcription factor RORγt and the helicase DDX5 at the Il17a and Il17f loci.
