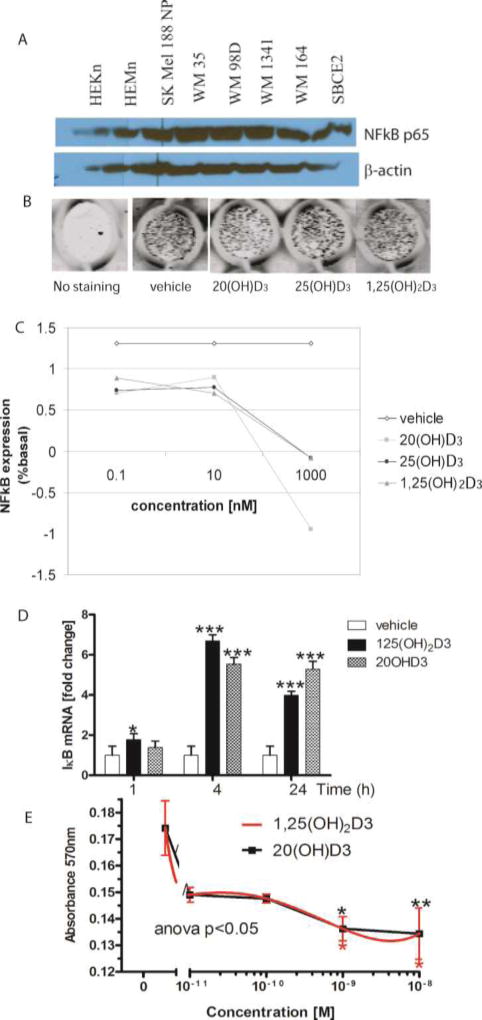
Figure 4. NF-kB as a target for bioregulation by hydroxyvitamin D3 in melanoma.
A. Basal expression of NF-kB in human melanoma lines and normal epidermal melanocytes and keratinocytes. Whole cell extracts were prepared from human melanoma lines or skin cells and were subjected to Western blotting as described previously [139, 148]. B-actin served as an internal control for equal amounts of proteins loaded onto the gel.
B, C. 20(OH)D3 decreases protein expression of NF-κB in keratinocytes in a dose-dependent manner. HaCaT keratinocytes were plated in a 96-well plate and incubated for 24 h with 1,25(OH)2D3, 20(OH)D3 or 25(OH)D3. Cells were fixed and stained with NF-κB antibody [148], followed by incubation with secondary IR antibody. The plate was scanned using an Odyssey infrared scanner (B) and data were analyzed using software for in-cell western (LI COR) (C).
D. Expression of the gene for IκBα (NF-kB inhibitor) is increased in human melanoma upon treatment with 1,25(OH)2D3 or 20(OH)D3. SKMel-188 cells were treated with 1,25(OH)2D3, 20(OH)D3 or ethanol (vehicle) for 1, 4 or 24 h. Cells were harvested for RNA isolation. cDNA was used for RT-PCR to test the expression of IκBα as described previously [139, 147, 148]. Reactions were performed using TaqMan. Cyclophillin B was used as internal control. Data were analyzed using the delta-delta CT method and presented as a fold change. Statistical analysis was performed using the t-test (*p<0.05; ***p<0.001) in comparison to vehicle.
E. 20(OH)D3 and 1,25(OH)2D3 inhibit growth of human melanoma cells. SKMel-188 cells were treated with 1,25(OH)2D3 or 20(OH)D3 at different concentrations (10−8–10−11 M) for 48 h. After incubation, the MTT assay was performed and absorbance was recorded at 570 nm. P<0.05*, p<0.01**, p<0.001***.