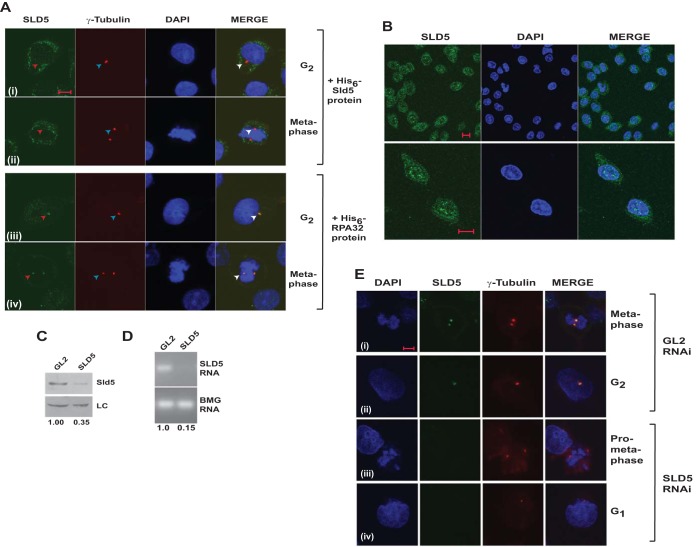
FIG 2.
Localization of Sld5 to centrosomes was confirmed by RNAi-mediated depletion. (A) Coimmunofluorescence assay of HeLa cells, as described in the legend to Fig. 1, was carried out in the presence of 5 ng/μl bacterially purified proteins. Preincubation with His6-Sld5 protein but not His6-RPA32 inhibited the localization of anti-Sld5 antibody to the centrosomes (red arrowheads). The top two rows demonstrate that after His6-Sld5 preincubation, the anti-Sld5 antibody was absent at the location where γ-tubulin stained, confirming that the antibody specifically binds to endogenous Sld5. (B) Coimmunofluorescence assay with Ab1 anti-Sld5 antibody without prepermeabilization showing nuclear localization of Sld5. The images were captured at different magnifications to show Sld5 localization in the entire field (top row) or individual cells (bottom row). (C) HeLa cells were transfected on three consecutive days with control GL2 or SLD5 siRNA, and the lysates were immunoblotted with anti-Sld5 antibody to confirm its specificity. LC, loading control showing equal protein loads in different lanes; the numbers indicate levels of Sld5 relative to control GL2 siRNA-transfected cells. (D) The decrease of SLD5 mRNA was confirmed by reverse transcriptase PCR. The numbers indicate the SLD5 mRNA levels following Sld5 depletion relative to control GL2 siRNA-transfected cells. Beta-2 microglobulin (BMG) served as the internal RNA-loading control. (E) HeLa cells were transfected on three consecutive days with control GL2 or SLD5 siRNA and costained for Sld5 (green), γ-tubulin (red), and DNA (blue) to confirm centrosomal localization of Sld5. (i and iii) Sld5 signal at mitotic centrosomes. (ii and iv) Sld5 signal at interphase centrosomes. Scale bars, 10 μm.