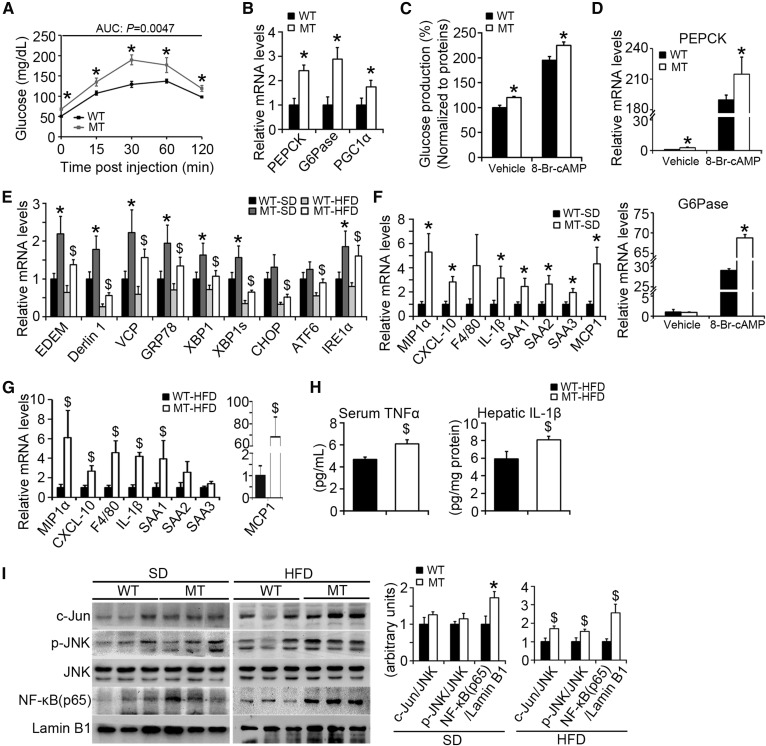
Fig. 7.
BAP31-deletion in hepatocytes enhances glucose production and increases ER stress and HFD-induced inflammation. A: Pyruvate tolerance test (PTT) was performed on WT and MT mice (16–18 weeks old). The blood glucose levels were determined via tail bleeding post pyruvate administration of 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min. AUCs (areas under the curve) were calculated (n = 6 per group). B: BAP31-deletion in hepatocytes induced PEPCK, G6Pase, and PGC1α mRNA levels in mouse livers (n = 6–7 per group). *P < 0.05, MT compared with WT mice fed SD. C: BAP31-deletion increased glucose production in the primary hepatocytes. The glucose concentrations have been normalized to cellular proteins. D: At the end of the incubation period, total RNA was extracted by using TRIzol reagent. The relative mRNA levels of PEPCK and G6Pase were determined by real-time PCR and normalized with 18S rRNA levels. *P < 0.05, MT compared with WT primary hepatocytes. E: The transcription levels of ER stress markers in WT and MT mice fed with SD or HFD. *P < 0.05, MT compared with WT mice fed SD. $P < 0.05, MT compared with WT mice fed HFD. F, G: Expression of markers of macrophages and pre-inflammatory genes were measured by real-time PCR in the livers from mice fed the SD or HFD for 96 days (n = 6–7 per group). H: BAP31-deletion in hepatocytes increased inflammatory cytokines. Serum TNFα (n = 6 per group) and hepatic IL-1β (n = 6 per group) in liver extracts were determined by ELISA. I: Immunoblot analysis of c-Jun, p-JNK, JNK, and NF-κB (p65) in the nuclei from the livers of mice fed the SD or HFD for 96 days. *P < 0.05, MT compared with WT mice fed SD. $P < 0.05, MT compared with WT mice fed HFD.