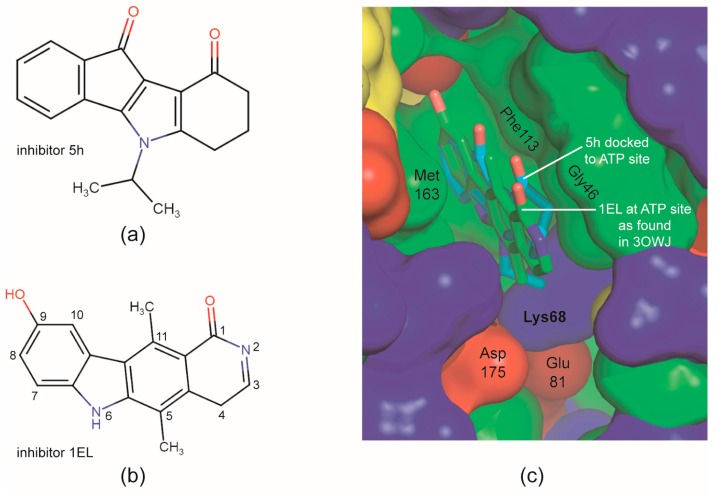
Figure 4.
In silico structure modelling of CK2α complexes with indeno[1,2-b]indole-type CK2 inhibitors according to Alchab et al. [58]. (a) 5-Isopropyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-indeno[1,2-b]indole-9,10-dione (5h), one of four indeno[1,2-b]indole-based inhibitors modelled into the ATP-site of CK2α by Alchab et al. [58]. (b) The pyridocarbazolone-type CK2 inhibitor 1EL that was co-crystallized with CK2α to give the complex structure 3OWJ [66] which served as a template for modelling of the CK2α/5h complex by Alchab et al. [58]. (c) Overlay of the X-ray structure of the CK2α complex with 1EL (green C-atoms; PDB 3OWJ) and the in-silico model of the CK2α complex of 5h (light blue C-atoms). Modified version of a picture originally published by Alchab et al. [58] with kind permission of MDPI AG, Basel, Switzerland.