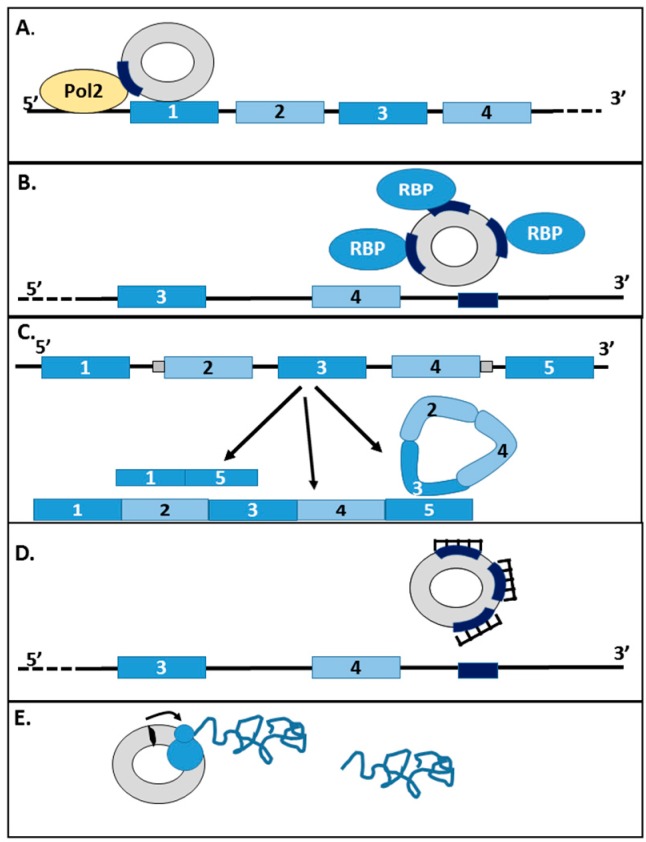
Figure 2.
Proposed roles of circRNA in the regulation of transcription and translation. circRNAs may regulate genes at several levels. (A) Firstly, nuclear circRNAs can interact with promoter regions of target genes and interact with RNA polymerase II (Pol2) to repress or enhance transcription; (B) Secondly, circRNAs can sequester RBPs that regulate mRNA processing and, thus, alter the splicing patterns of the genes in question, or moderate mRNA stability. RBP binding sites are given by dark blue boxes; (C) Thirdly, the biogenesis of circular RNAs may results in the production of a linear RNA lacking the circularised exons. The formation of circRNAs can thus reduce the amount of linear transcript produced; (D) circRNAs can act as micro RNA (miRNA) sponges, sequestering them away from their binding sites in target genes, which are given by dark blue boxes; (E) Circular RNAs can also be translated. The initiation codon is given by a black oval, and the translating ribosome and nascent polypeptide are indicated.