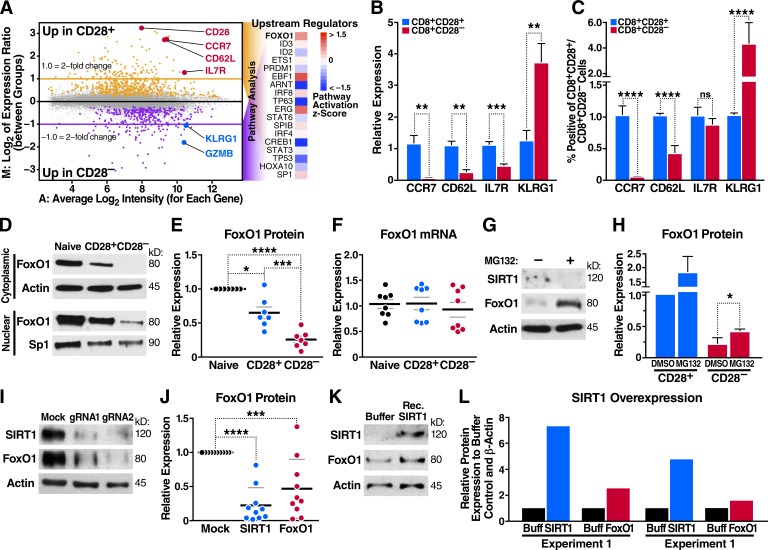
Figure 3.
Altered FoxO1 gene expression in CD8+CD28– T cells. (A) Microarray analysis in CD8+CD28+ and CD28– T cells, predicting FoxO1 as an altered transcriptional regulator in CD8+CD28– T cells. (B) CCR7, CD62L, IL7R, and KLRG1 mRNA were assessed by qRT-PCR and normalized to RPL13A mRNA from sorted human T cell populations (n = 5, paired one-way ANOVA). (C) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained for CD3, CD8, CD28, and indicated markers as in B and analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 5, paired one-way ANOVA). (D and E) FoxO1 expression in sorted human T cells was measured by Western blot (representative, n = 7, paired two-tailed Student’s t test). (F) FoxO1 mRNA was analyzed by qRT-PCR and normalized to RPL13A (n = 8). (G and H) CD28+ and CD28– T cells were treated with 20 µM MG132 for 6 h, and FoxO1 expression was measured by Western blot (n = 3, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, G shows CD28– T cells). (I and J) SIRT1 knockdown by Cas9–RNP nucleofection and Western blot for SIRT1 and FoxO1 expression (n = 9, two-way ANOVA). (K) Nucleofection of recombinant SIRT1 protein into CD8+ T cells and Western blot for SIRT1 and FoxO1 protein 18 h after nucleofection (representative, n = 2). (L) Densitometry of two independent experiments (n = 2). Data are mean ± SEM of individual donors. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.000. ns, not significant.