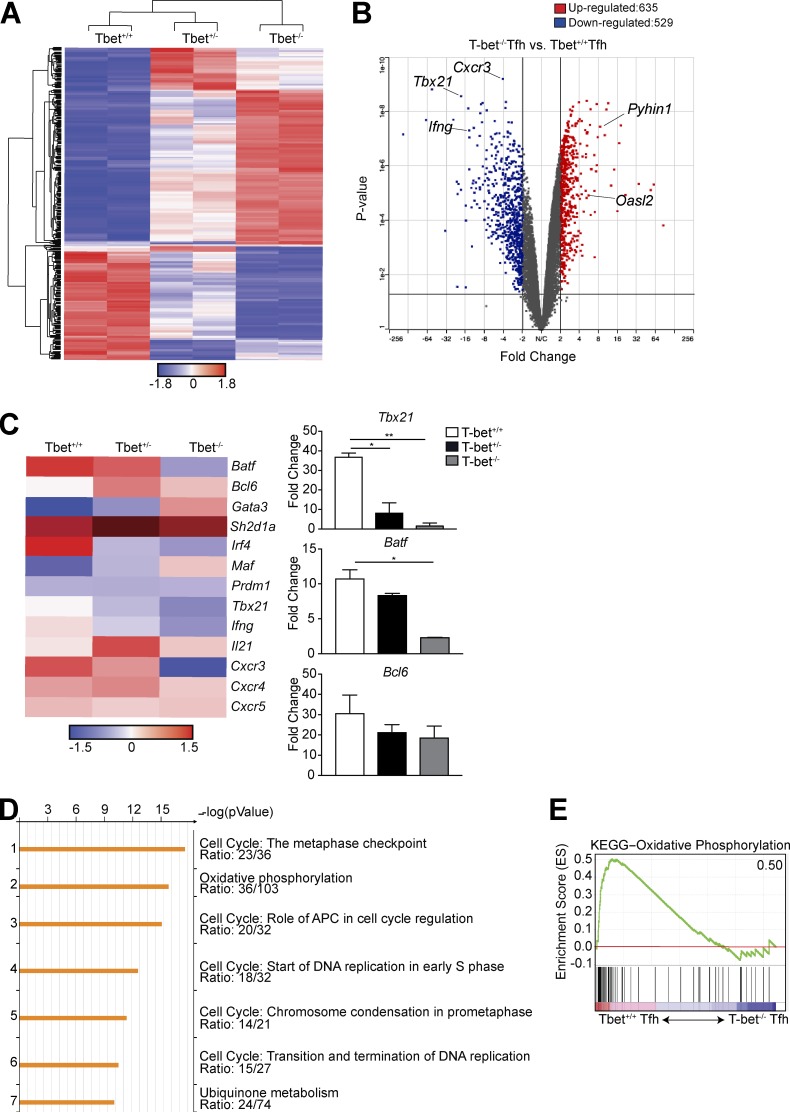
Figure 4.
T-bet is required for proper transcriptional development of Tfh cells. T-bet+/+, T-bet+/−, or T-bet−/− Thy1.1+ Stg CD4+ T cells were transferred into Thy1.2+ B6 mice with LCMV Armstrong infection 24 h later. Spleens were harvested 8 d p.i. (A) Heat map of significantly differentially expressed genes (rows) in the three populations (columns). FDR, α < 0.05. (B) Volcano plot of gene expression comparing T-bet+/+ with T-bet−/− Ly6cloPSGL-1loCXCR5hiPD-1hi Tfh cells to identify differentially expressed genes with a cutoff p-value of <0.05, fold change >2, comparing T-bet+/+ or T-bet−/− cells. (C) Heat map of selected T cell–related genes. FDR-adjusted q < 0.05 comparing T-bet+/+ or T-bet−/− Tfh cells. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of selected T cell–related genes, normalized to results obtained for the control gene Hprt. Data from two independent sorts using 10 mice each; fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM). (D) Enrichment pathways analysis of the down-regulated genes in T-bet−/− Tfh cells, with the top seven pathways listed, including the enrichment p-value and the number of genes per total genes in a pathway. (E) Enrichment of gene signatures related to activation of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes oxidatve phosphorylation pathway in T-bet+/+ versus T-bet−/− Tfh cells. Number in top-right corner is the enrichment score; all p-values and FDRs = 0. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. Error bars represent SEM.