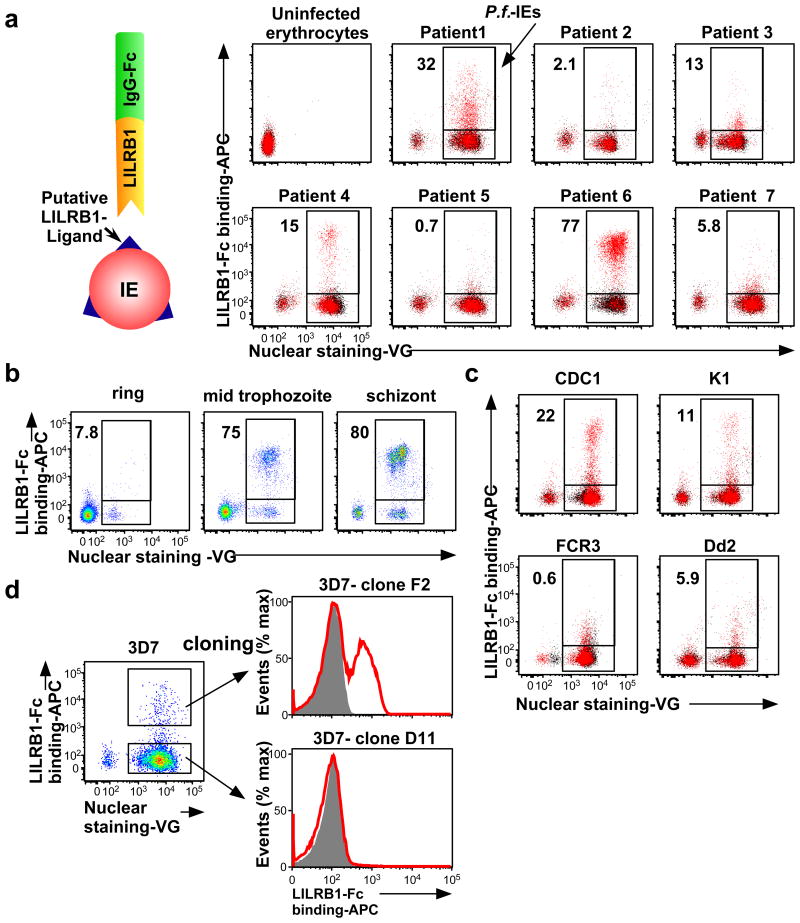
Figure 1. Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes (IEs) are recognised by LILRB1.
a, Analysis of IEs with an LILRB1-Fc fusion protein. Diagram of LILRB1-Fc binding to IEs. Schizont-stage P. falciparum IEs and uninfected erythrocytes were stained with LILRB1-Fc (red dot) and control-Fc (black dot), followed by Vybrant Green (VG) staining. Percentages of LILRB1-binding IEs are shown. b, Different stages of P. falciparum IEs derived from patient 6 were stained with LILRB1-Fc, followed by VG staining. Percentages of LILRB1-positive IEs are shown. c, Schizont-stage IEs from four P. falciparum laboratory strains were stained with LILRB1-Fc (red) and control-Fc (shaded), followed by VG staining. Percentages of LILRB1-binding IEs are shown. d, LILRB1-binding clone 3D7 (F2) and non-binding clone 3D7 (D11). Red and shaded histograms indicate staining with LILRB1-Fc and control-Fc, respectively. Data represent at least three independent experiments and the variabilities of data shown a, b and c are shown in Extended Data Figure 2a, 2b and 2c, respectively.