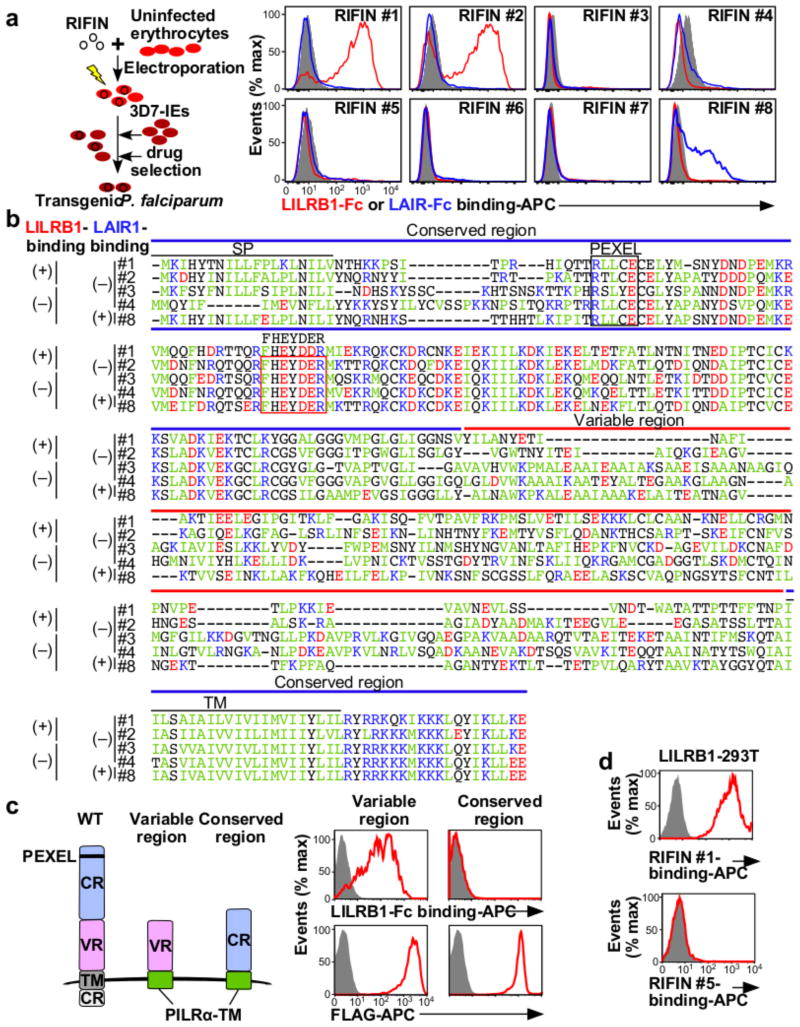
Figure 2. RIFINs are ligands for LILRB1 and LAIR1.
a, Diagram of the method used to generate transgenic P. falciparum. LILRB1-Fc and LAIR1-Fc bind IEs expressing RIFIN-transgenes. RIFIN-transgenic parasites are RIFIN #1: PF3D7_1254800, RIFIN #2: PF3D7_0223100, RIFIN #3: PF3D7_0500400, RIFIN #4: PF3D7_1000500, RIFIN #5: PF3D7_1254200, RIFIN #6: PF3D7_1400600, RIFIN #7: PF3D7_1040300 and RIFIN #8: PF3D7_1101100. Red, blue and shaded histograms indicate staining with LILRB1-Fc, LAIR1-Fc and control-Fc, respectively. b, Amino acid sequence alignments of RIFINs that bind LILRB1, LAIR1 or neither. SP and TM indicate the signal peptide and transmembrane domains, respectively. Green, blue, red and black characters indicate hydrophobic, basic, acidic and neutral amino acid residues, respectively. The FHEYDER sequence is contained in the red box. c, N-terminally FLAG-tagged conserved or variable regions of LILRB1+ RIFIN #1 fused to the PILRα transmembrane region (TM) expressed by 293T cells were tested for LILRB1-Fc binding (upper panel). RIFIN expression was detected using an anti-FLAG antibody (lower panel). Red and shaded histograms indicate RIFIN and mock (GFP) transfectants, respectively. d, LILRB1-transfected 293T cells were stained with His-tagged LILRB1+ RIFIN #1 or LILRB1− RIFIN #5, followed by staining with an anti-His antibody. Data represent at least three independent experiments.