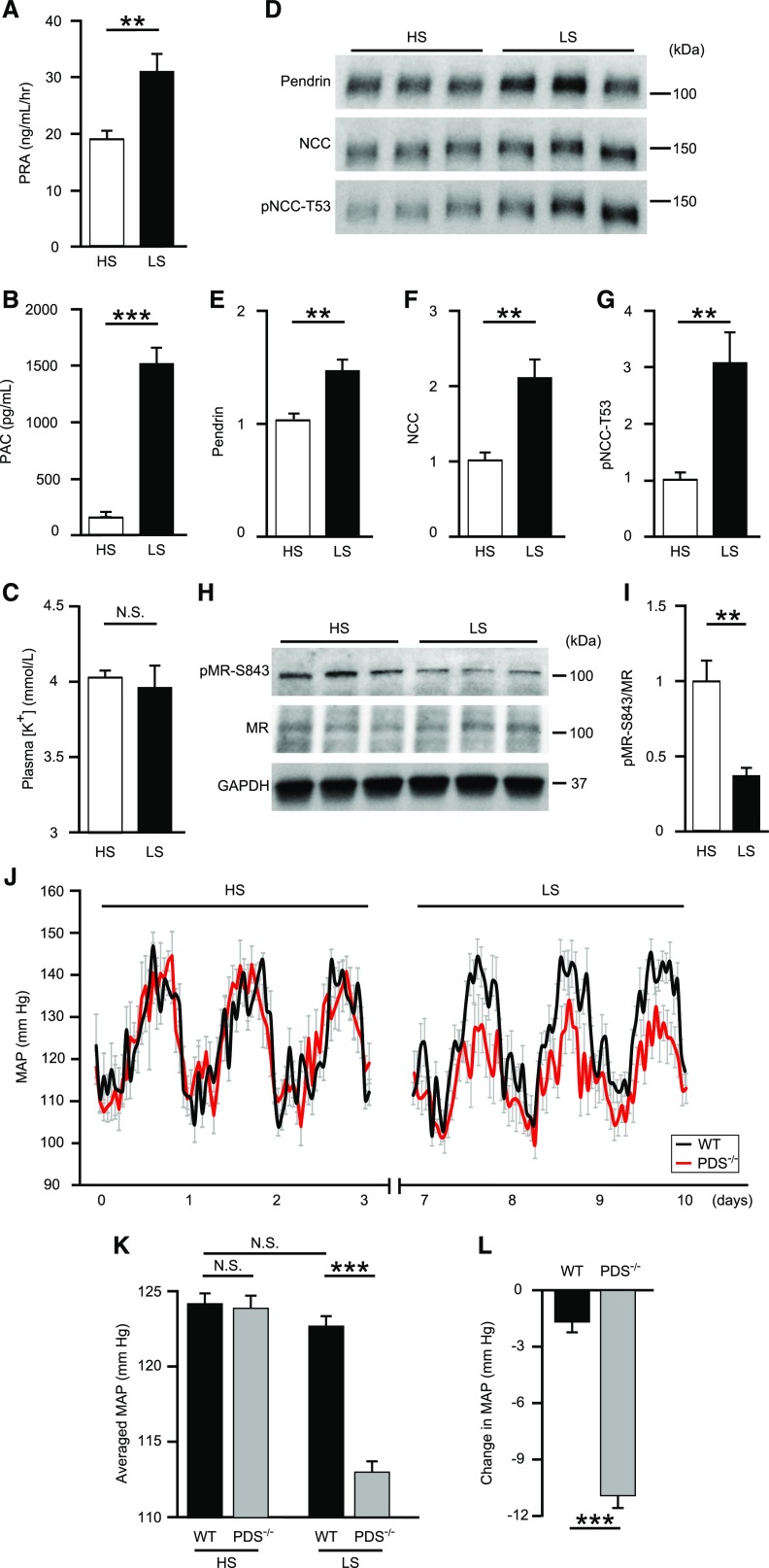
Figure 1.
Activation of the RAAS by NaCl restriction increases pendrin and decreases pMR-S843 levels, and pendrin contributes to maintaining normal BP in cooperation with NCC during volume depletion. (A) PRA, (B) PAC, and (C) plasma [K+] in C57BL/6J mice fed HS (n=9) or LS (n=8) diets. (D) Representative Western blots and quantification of (E) pendrin, (F) NCC, and (G) pNCC-T53 in the membrane fraction of kidneys from mice fed HS (n=6) or LS (n=7) diets. Equal loading was confirmed by parallel Coomassie-stained gels (see Supplemental Figure 3). Representative (H) Western blots and (I) quantification of pMR-S843 levels in the whole-kidney lysates from mice fed HS and LS diets. (J) Hourly averaged MAPs measured over three consecutive days in mice fed HS or LS diets, (K) averaged MAPs of mice fed HS or LS diets, and (L) changes in the MAPs of PDS−/− (n=5) and WT mice (n=5) fed HS or LS diets. MAP tracings represent averages of measurement from all animals. For (A–I), statistical comparisons were performed using an unpaired t test. For (J–L), statistical comparisons were performed using a two-way ANOVA, followed by Holm–Sidak multiple comparison tests. Data represent the mean±SEM. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. PAC, plasma aldosterone concentration; PRA, plasma renin activity.