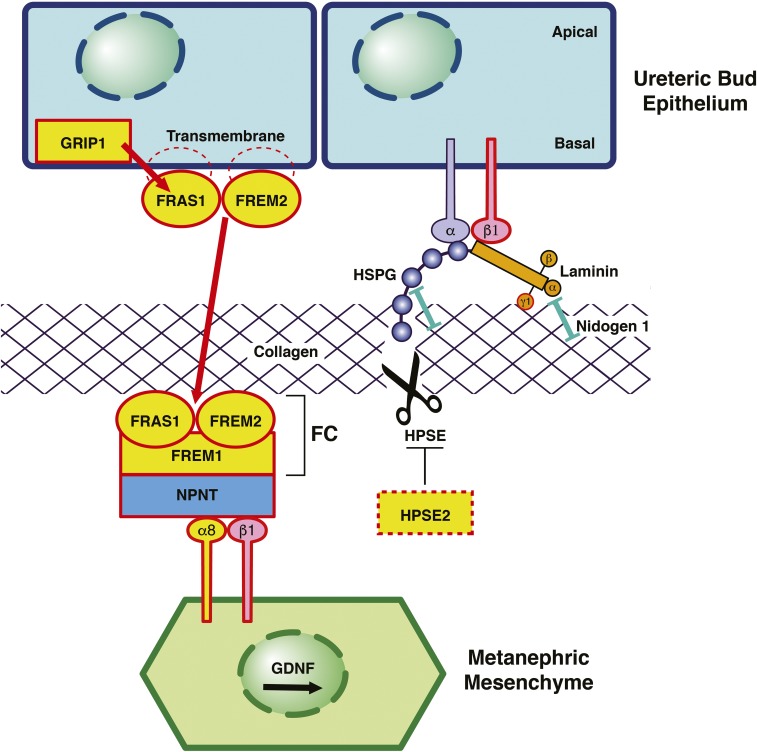
Figure 2.
ECM proteins cause murine and human CAKUT. Schematic of the interface between the UB and the MM in renal development. Proteins encoded by genes that, if mutated, cause monogenic CAKUT in humans are highlighted in yellow. Red frames indicate proteins encoded by genes mutated in CAKUT in mice. (Left panel) FRAS1 and FREM2 localize in epithelial cells of the UB as transmembrane proteins with intracytoplasmic tail regions.41,98,103 The interaction with PDZ domains of the intracellular protein GRIP1 is essential for targeting to the basal surface of the UB cells and shedding of FRAS1 from the membrane.98,107 FREM1 is produced by the MM and secreted into the extracellular space.106,107 FRAS1, FREM2, and FREM1 assemble at the epithelial-mesenchymal interface to form the FC.107 Mutations in the genes encoding these proteins cause CAKUT (Supplemental Figure 2). Also, mutations in GRIP1 result in human and murine CAKUT. Nephronectin (NPNT) functions as an adaptor to interconnect the ternary FC with the ITGA8/integrin-β1 heterodimer on the surface of MM cells. ITGA8/integrin-β1 signaling leads to an increased expression of GDNF by the MM, thereby promoting renal morphogenesis.183 Mutations in ITGA8 in humans and mice cause CAKUT.44 Loss of FC integrity results in a significant decrease in GDNF expression in the MM, thereby hampering the interaction between the UB and the MM and consequentially, impeding renal morphogenesis.183 (Right panel) Laminins are cross-shaped ECM molecules that consist of three distinct chains (α, β, and γ).101 Laminins simultaneously interact with cell surface receptors (integrins), HSPG, collagen, and nidogen 1 (see box).184 Laminins that contain γ1-chains form high-affinity interactions with nidogen 1.101 Fourteen distinct laminin isoforms have been identified to date, of which ten possess the laminin-γ1 chain.101,185 A homozygous ablation of the nidogen binding site in laminin-γ1 has been shown to result in severe CAKUT phenotypes (including bilateral renal agenesis) in mice.101 Despite its important role in ECM assembly, targeted inactivation of nidogen 1 did not result in a CAKUT phenotype.101 Both nidogen 1 and Laminin are known interactors of HSPG. HPSE is one of the few enzymes with the ability to break down HSPG.115 Knockdown of neither HSPG nor HPSE has been reported to cause CAKUT phenotypes in mice.115,120,186,187 However, recessive mutations in HPSE2 have been identified in human patients with urofacial syndrome,43,93 with a similar phenotype in mice.43 Although HPSE2 has no detectable enzymatic activity itself, it has been shown to function as an endogenous inhibitor of HPSE (Supplemental Figure 3).116 Modified from refs. 107 and 184, with permission.