Fig. 3.
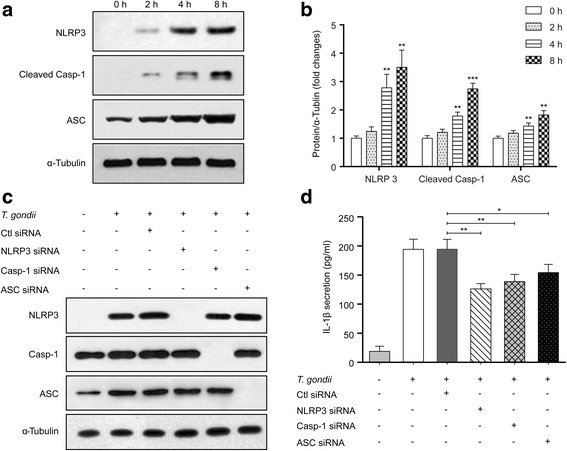
Toxoplasma gondii induces IL-1β production in FHs Int 74 cells via activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. FHs 74 Int cells were infected with T. gondii at an MOI of 10 for 0, 2, 4 or 8 h. The cells were then collected and analyzed for NLRP3, cleaved Casp-1 and ASC protein levels by Western blotting. a Representative blots depicting NLRP3, cleaved Casp-1 and ASC protein levels in mock-infected or T. gondii-infected FHs 74 Int cells (α-Tubulin served as an internal control for protein loading). b Bar plot depicting the NLRP3/α-Tubulin, cleaved Casp-1/α-Tubulin and ASC/α-Tubulin ratios as determined by densitometric analysis of Western blotting and expressed as fold change compared with the mock-infection control. For all panels, data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with mock-infection control. FHs 74 Int cells were transfected with NLRP3, Casp-1, ASC or control siRNAs and then infected with T. gondii at an MOI of 10 for 8 h. c Cell extracts were subjected to Western blotting to detect NLRP3, Casp-1 and ASC protein levels. d The cell culture supernatants were collected and assayed for IL-1β levels by ELISA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with control siRNA-transfected T. gondii-infected cells. All data shown are representative of three independent experiments
