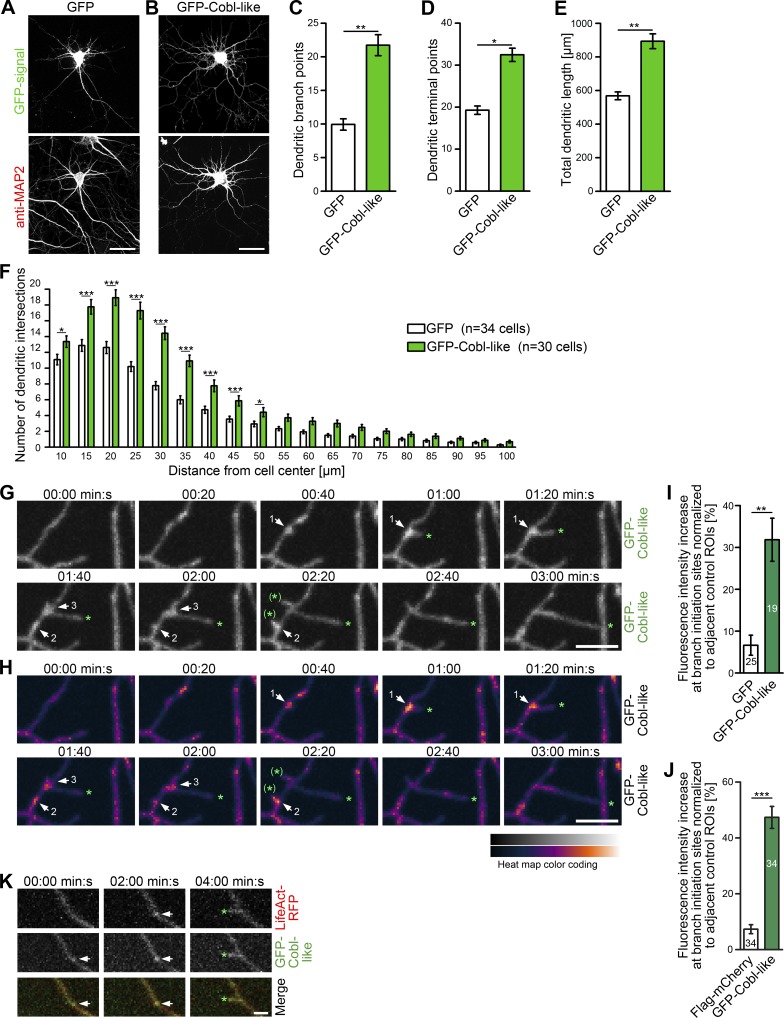
Figure 3.
Cobl-like promotes the formation of the dendritic arbor of primary hippocampal neurons. (A and B) Morphology of Cobl-like–overexpressing hippocampal neurons (DIV7). Bars, 20 µm. (C–F) Quantitative determinations of indicated dendritic arbor parameters (C–E) and Sholl analyses (F). (G) MIPs of individual frames of a 3D time-lapse recording of dendrites of DIV7 neurons with GFP-Cobl-like enrichments (distinct sites, white arrows; numbering marks individual events) seconds before protrusion initiation from these sites. Tips of growing dendritic protrusions are marked by a green asterisk. Abandoned protrusive events are marked by a green asterisk in brackets. (H) Heat map representation of data in G. Bars, 5 µm. (I and J) Quantitative evaluations of dynamic Cobl-like enrichment at branch initiation sites 30 s before protrusion formation in comparison to the behavior of GFP used as control (I) and in comparison to directly cotransfected Flag-mCherry firmly excluding theoretical volume artifacts (J), respectively. (K) MIPs of single frames of a 3D time-lapse recording of neurons cotransfected with GFP-Cobl-like and LifeAct-RFP (visualizing F-actin). See the explanation of panel G for the meaning of the markings. Bar, 2 µm. Data are mean ± SEM, two-tailed Student’s t test (C–E, I, and J) and two-way ANOVA plus Bonferroni’s post test (F). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.