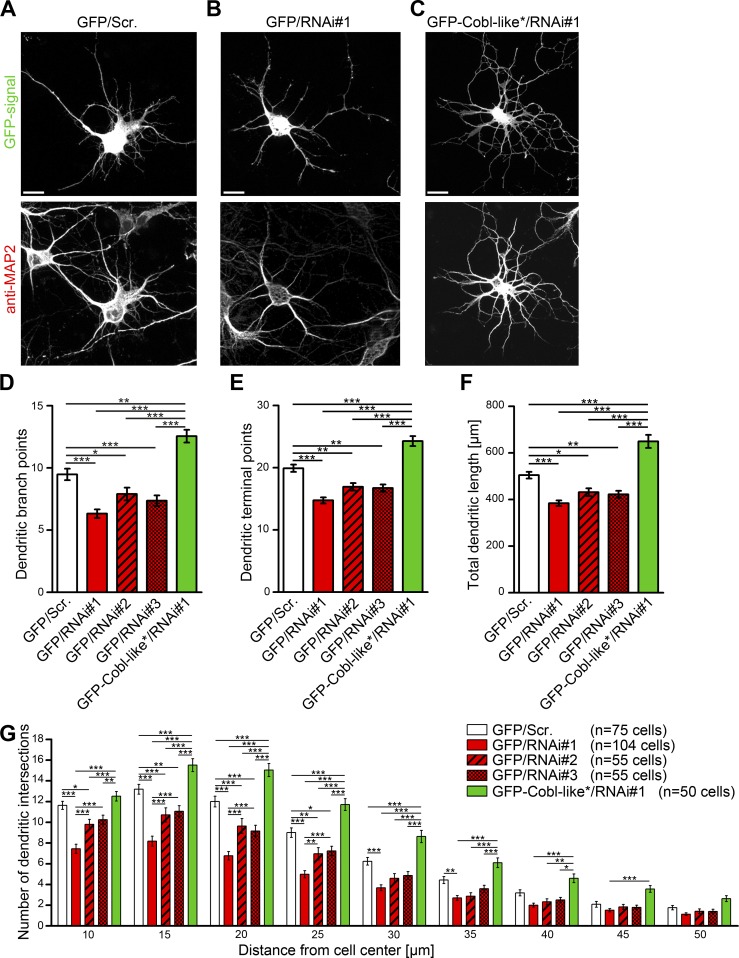
Figure 4.
Cobl-like is critical for dendritic arbor formation. (A–C) Morphology of Cobl-like–depleted neurons (RNAi#1; B) in comparison to control neurons (scrambled RNAi sequence; Scr.; A) and to neurons coexpressing an RNAi#1-insensitive Cobl-like mutant (Cobl-like*; rescue; C). Bars, 10 µm. (D–F) Quantitative determinations of specific defects in dendritic arborization caused by Cobl-like addressing dendritic branch points (D), dendritic terminal points (E), the summarized length of the dendritic arbor (F), and Sholl intersections (G). Data are mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA Tukey’s post test (D–F) and two-way ANOVA plus Bonferroni’s post test (G). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.