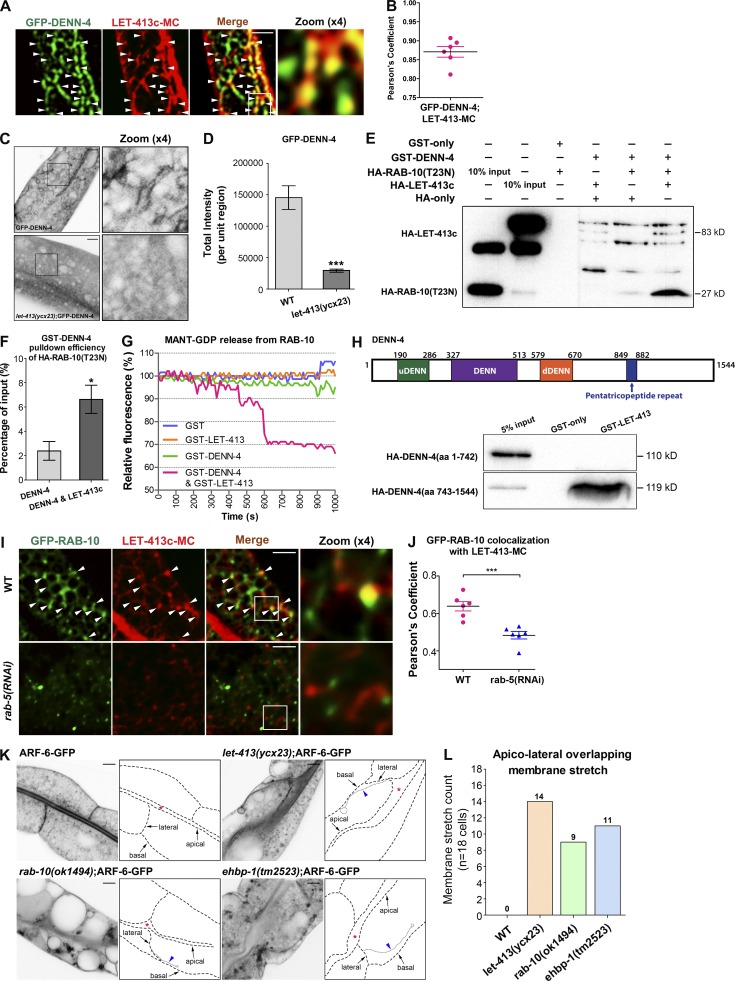
Figure 6.
LET-413 facilitated the interaction of DENN-4 with RAB-10(GDP), and the intestinal cells’ lateral membrane organization was distorted in let-413 and recycling regulator mutants. (A and B) GFP-DENN-4 and LET-413c-mCherry displayed significant colocalization on punctate structures. Pearson’s correlation coefficient for GFP and mCherry signals is calculated (n = 6 animals). (C and D) Loss of LET-413 led to the cytosolic dispersal of GFP-DENN-4. Error bars represent SEM (n = 18 each). Asterisks indicate significant differences (***, P < 0.001; one-tailed Student’s t test). (E) In the presence of LET-413, the affinity of GST-DENN-4 for HA-RAB-10(T23N) was significantly elevated. (F) GST-DENN-4 pull-down efficiency of HA-RAB-10(T23N) with LET-413c was increased by approximately threefold. The SEMs from three independent experiments are shown. Asterisks indicate significant differences (*, P < 0.05; one-tailed Student’s t test). (G) In vitro GEF assay. MANT-GDP release from RAB-10 was measured by adding GST-LET-413, GST-DENN-4, and GST-DENN-4&GST-LET-413. (H) LET-413c lacks binding to the fragment containing DENN domain (aa 1–742) but has a significant interaction with the C-terminal fragment of DENN-4 (aa 743–1544). (I and J) The colocalization of LET-413c-mCherry with GFP-RAB-10 in wide-type (∼64% overlap) and rab-5(RNAi) (∼48% overlap) animals was compared. Pearson’s correlation coefficients for GFP and mCherry signals are calculated (n = 6 animals). Error bars represent SEM. ***, P < 0.001. (K) Intestinal cells’ lateral membranes (labeled by ARF-6-GFP) were distorted in let-413, rab-10, and enbp-1 mutants. Arrows indicate apical, basal, and lateral plasma membranes. Arrowheads indicate the overextended lateral membrane. (L) Overextended lateral membranes were quantified. Numbers of lateral membrane overextensions in 18 intestinal cells (total of six animals per each genotype) were quantified and plotted. Bars, 10 µm.