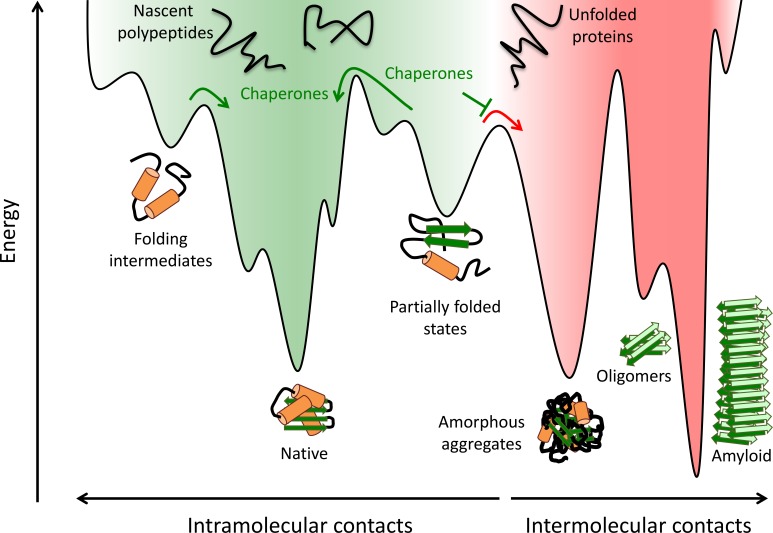
Figure 2.
Protein folding and aggregation. Nascent polypeptides fold by sampling various conformations and sequestering hydrophobic amino acid residues. Partially folded intermediates, both on- and off-pathway, can become trapped in localized energy minima. These species are at risk of aggregation by forming aberrant intermolecular contacts, which can lead to the formation of oligomers, amorphous aggregates, and amyloid fibrils. Molecular chaperones promote the formation of the native species by lowering free-energy barriers between kinetically stable intermediates, smoothing the protein folding landscape (green arrows), and preventing aberrant intermolecular interactions (red arrow). Adapted from Balchin et al. (2016), Hartl et al. (2011), and Kim et al. (2013).