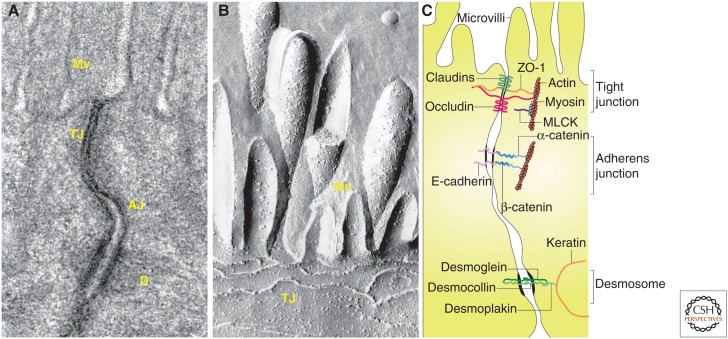
Figure 2.
The apical junctional complex. (A) Transmission electron micrograph showing junctional complexes between two villous enterocytes. The tight junction (TJ) is just below the microvilli (Mv), followed by the adherens junction (AJ). The desmosomes (D) are located basolaterally. (B) Freeze-fracture electron micrograph showing apical microvilli (Mv) and tight junction strands (TJ) in a cultured intestinal epithelial cell. (C) Line drawing of the apical junctional complex of an intestinal epithelial cell. Tight junction proteins include claudins, zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), and occludin, whereas E-cadherin, α-catenin, and β-catenin interact to form the adherens junction. Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) is associated with the perijunctional actomyosin ring. Desmosomes are formed by interactions between desmoglein, desmocollin, desmoplakin and keratin filaments. (Parts A and C, from Turner 2009; reprinted, with permission; part B, from Shen et al. 2011; reprinted, with permission from Annual Reviews ©2011.)