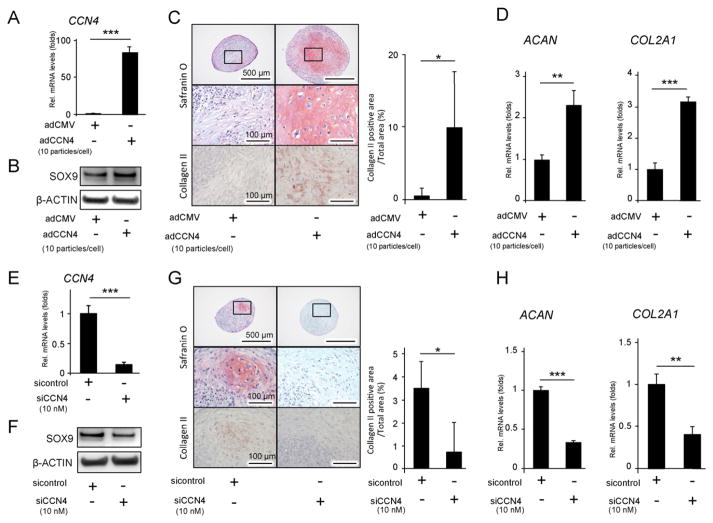
Fig. 2.
The effect of CCN4 on the chondrogenic differentiation of hBMSCs in vitro. hBMSCs were transduced with adCCN4 (A–D) or siCCN4 (E–H) for two days, and cultured in micromasses. (A, E) Two days after the transduction, mRNA expression levels of CCN4 gene were measured by real-time RT-PCR. (B, F) The cellular proteins were collected 24 h after chondrogenic induction, and protein levels of SOX9 were detected by western blot. β-ACTIN was used as protein loading control. (C, G) Twenty eight days after chondrogenic induction, histological analysis of hBMSC micromass cultures was performed for detection of glycosaminoglycans with safranin O staining, or collagen type II by immunohistochemistry. Graphs show the quantitation of the positive area of collagen type II. (D, H) mRNA expression level of ACAN COL2 gene was measured by real time RT-PCR. The expression of each gene was normalized to that of S29 ribosomal RNA. Bars represent the mean values and standard deviation (+/−SD) (n = 3). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (Student’s t-tests). Results are representative data of at least three independent experiments.