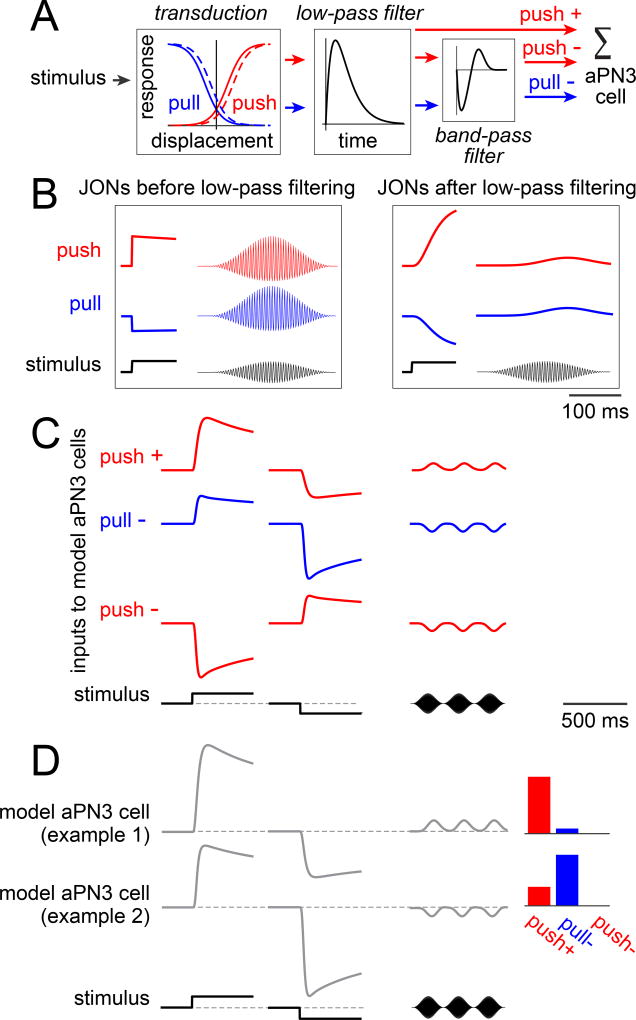
Figure 5. Linear combinations of peripheral inputs can account for many features of aPN3 neuron responses.
A) Model components. Different model aPN3 neurons are generated by varying the weights on the three inputs to aPN3 neurons (push+, pull−, push−); all other parameters are fixed.
B) Responses of model JONs before and after low-pass filtering. Shown here are responses to a sustained displacement and a 200 Hz sinusoid modulated at 4 Hz. Note that the push and pull JONs are anticorrelated in response to the sustained displacement, but positively correlated in response to sound. (Here, the pull channel has not yet passed through the bandpass filter, so the dynamics of the pull and push channels are still identical.)
C) The three inputs to model aPN3 neurons. Responses to three stimuli are shown here: a positive displacement of 2 µm, a negative displacement of 2 µm, and a sound stimulus (a 200 Hz sinusoid modulated at 4 Hz). The push+ and pull− inputs are positively correlated in response to a sustained displacement but negatively correlated in response to sound. Note that the time scale of this and the subsequent panel are compressed five-fold relative to (B). Adaptation in the excitatory input is due to the horizontal shift of the sigmoid curves; additional adaptation in the two inhibitory inputs are due to the bandpass filter.
D) Responses of two different model aPN3 neurons. These two models are illustrative examples because they combine the same two input channels (push+ and pull−) but with different weights. Bars at right represent the weights on the input channels. These model aPN3 neurons are positively correlated in response to a sustained displacement but negatively correlated in response to sound.