Figure 1. Published models of full-length lipid-free human apoA-I.
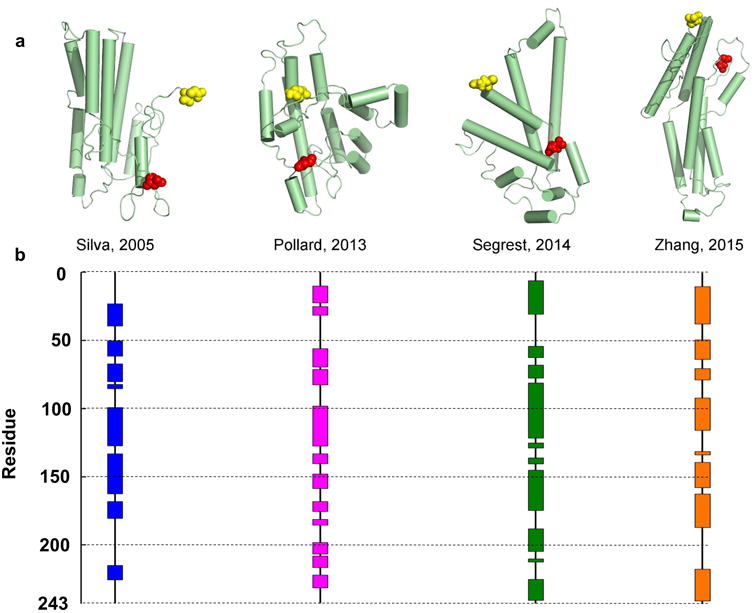
There are 8 published models of lipid-free monomeric apoA-I that have coordinates available. Silva et al.11 proposed a model based on chemical cross-linking and homology sequence threading techniques. Pollard et al.16 generated their model using chemical cross-linking and cysteine point mutations. Segrest et al.10 used chemical cross-linking and molecular dynamics simulations using information from the crystal structures of apoA-I truncation mutants as templates. Note: this paper also proposed 3 other models that differed in terms of length of simulation (one of which is shown here, 15 ns). Zhang et al.17 produced molecular simulations using information from the crystal structures as initial templates. The models are shown in cartoon form with cylinders representing helical domains in panel (a). The N-terminal amino acids are shown space-filled in red while the C-terminal amino acids are in yellow. The alpha helical content of each model (as assessed by Pymol) is shown on the linear diagram for each model in panel (b) with each colored block representing helical domains and black lines representing random coil or loop regions.
