Figure 5. Predictions of the new model with respect to proteolytic susceptibility and stability.
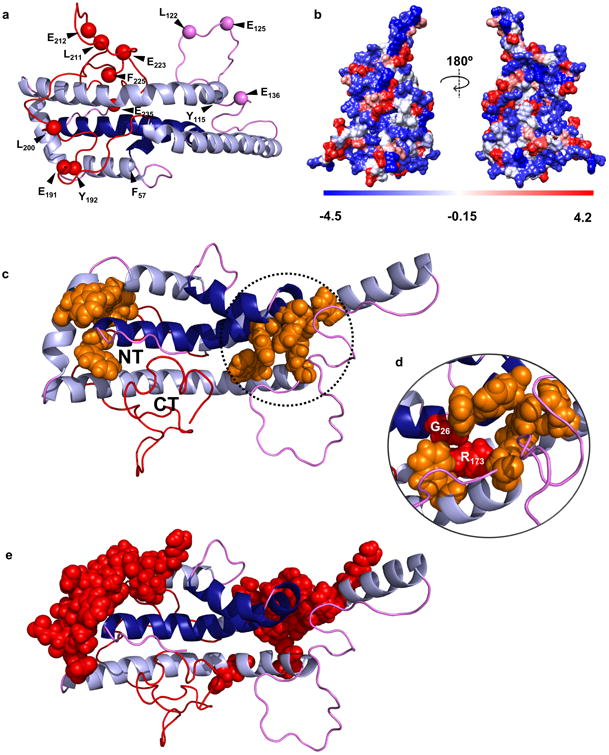
Panel (a) shows the proteolytic cleavage sites from Supplementary Table 6. Panel (b) shows a space-filled rendering of the model by residue hydrophobicity with hydrophilic residues in blue and hydrophobic residues in red. Panel (c) highlights aromatic clusters (orange) that may participate in molecular stabilization and the proximity of the N- and C-termini in the time-averaged model. Panel (d) shows the position of natural mutations in apoA-IIOWA (Gly 26) and apoA-IMilano (Arg 173) within one aromatic cluster. Panel (e) shows critical stabilizing residues mapped by Gorshkova et. al. for lipid-free apoA-I33,42.
