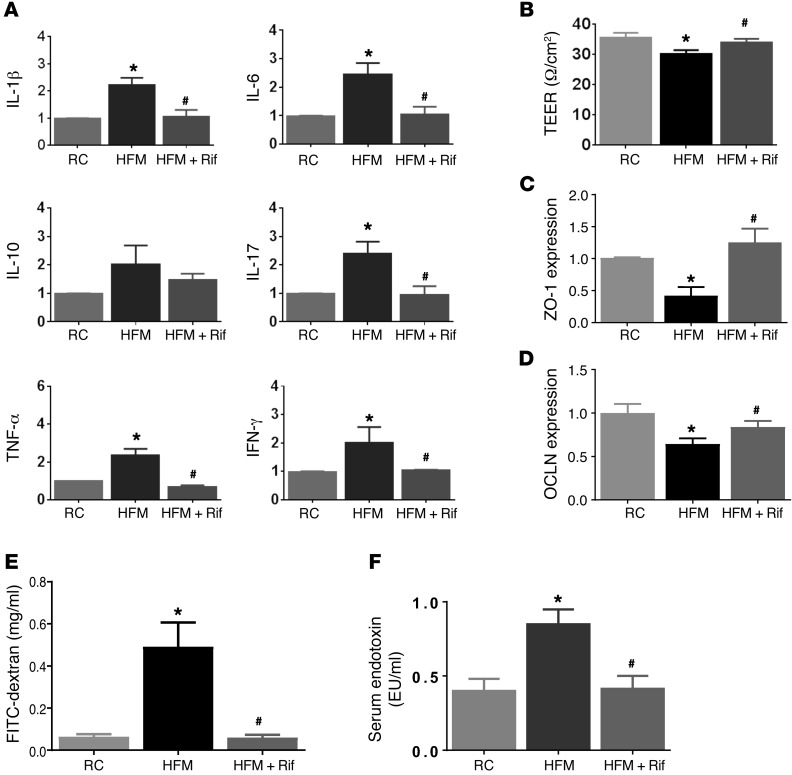
Figure 1. Effects of HFM on cytokine expression and gut permeability of the rat colon.
(A) RT-PCR measurement of cytokines in rats fed for 2 weeks with RC, HFM, or HFM with rifaximin (HFM+Rif). mRNA levels represented as fold change in each target mRNA after normalization to GAPDH. HFM induced increases in IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, TNF-α, and IFN-γ gene expression, indicating low-grade mucosal inflammation. (B) HFM increased gut permeability, as measured by TEER. (C) HFM caused decreased ZO-1 and (D) OCLN expression. (E) HFM increased the appearance of FITC–dextran in serum, accompanied by increased serum LPS (F), indicating endotoxemia. Rifaximin prevented HFM-induced changes in cytokine, gut permeability, and endotoxemia (A–E) (n = 6 per group). *P < 0.05 versus RC; #P < 0.05 versus HFM. HFM, high-FODMAP diet; OCLN, occludin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; RC, regular chow; TEER, transepithelial electrical resistance. P values determined by 2-tailed Student’s t test.