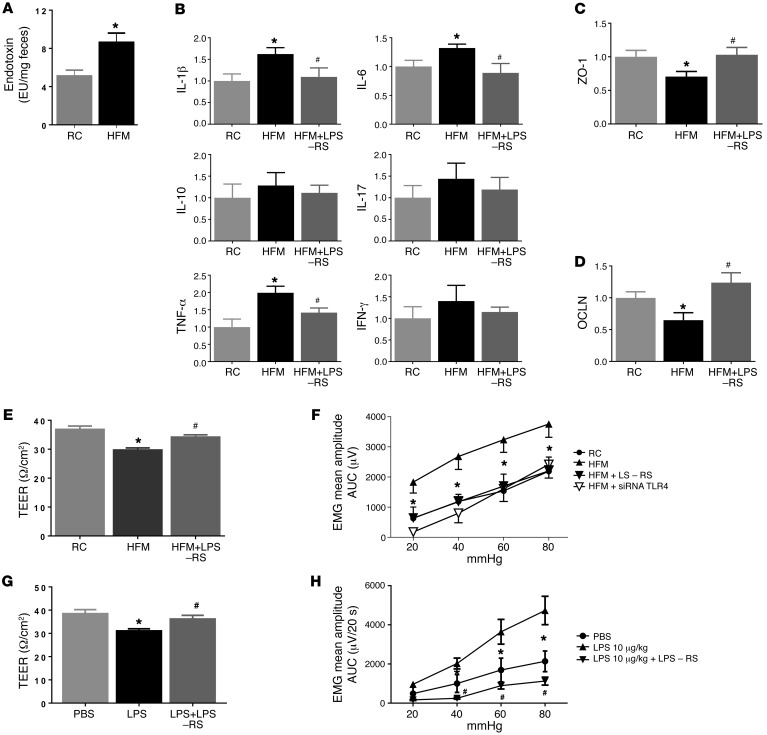
Figure 4. Effects of fecal supernatant from HFM rats and LPS on gut permeability and visceral sensitivity.
(A) Endotoxin level (LPS) in fecal contents was elevated in HFM compared with RC rats (n = 6) *P < 0.05. (B–D) Intracolonic infusion of fecal supernatant from HFM rats caused changes in cytokines and junction proteins, ZO-1 and OCLN. These changes were prevented by LPS antagonist, LPS-RS. (E) HFM fecal supernatant decreased the transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER), indicating an increase in epithelium permeability of colon mucosa in naive rats (n = 6, P < 0.05). This increase was prevented by LPS-RS. (F) Intracolonic infusion of fecal supernatant from HFM rats induced visceral hyperalgesia in naive rats; this was prevented by LPS-RS or siRNA targeting TLR4 (n = 6, P < 0.05). (G) Intracolonic LPS infusion induced increased epithelium permeability of colonic mucosa (i.e., reduced TEER) in naive rats; this was prevented by LPS-RS. (H) Intracolonic infusion of LPS (10 μg/kg) induced visceral hyperalgesia in naive rats; this was prevented by LPS-RS (100 μg/kg). *P < 0.05 versus RC or PBS treated; #P < 0.05 versus HFM-supernatant or LPS treated. AUC, area under the curve; EMG, electromyographic activity; HFM, high-FODMAP diet; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; RC, regular chow; siRNA, small (or short) interfering RNA; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4. P < 0.05, by 2-tailed Student’s t test or 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA.