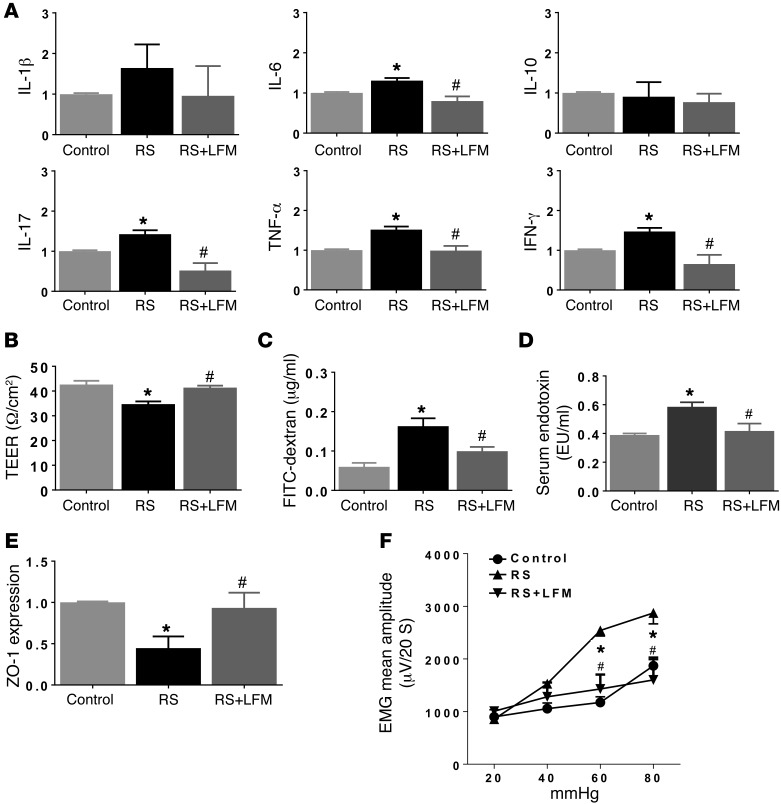
Figure 6. Effects of LFM on RS-induced mucosal inflammation, permeability alteration, and visceral hypersensitivity.
(A) RS caused mucosal inflammation characterized by increased cytokine expression. LFM prevented these changes. RS increased colon permeability, as measured by TEER (B) and FITC–dextran in serum (C), accompanied by increased serum LPS (D), indicating endotoxemia. (E) RS caused a decrease in ZO-1 expression. LFM prevented RS-induced changes in cytokine levels, gut permeability, and endotoxemia (A–E). (F) RS caused an increase in the visceromotor response to colorectal distension, compared with sham RS controls. LFM prevented RS-induced visceral hypersensitivity. n = 6 per group. *P < 0.05 compared with sham RS as control and RS+LFM; #P < 0.05 compared with RS. AUC, area under the curve; EMG, electromyographic activity; LFM, low-FODMAP diet; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; RS, restraint stress; TEER, transepithelial electrical resistance. P < 0.05, by 2-tailed Student’s t test or 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA.