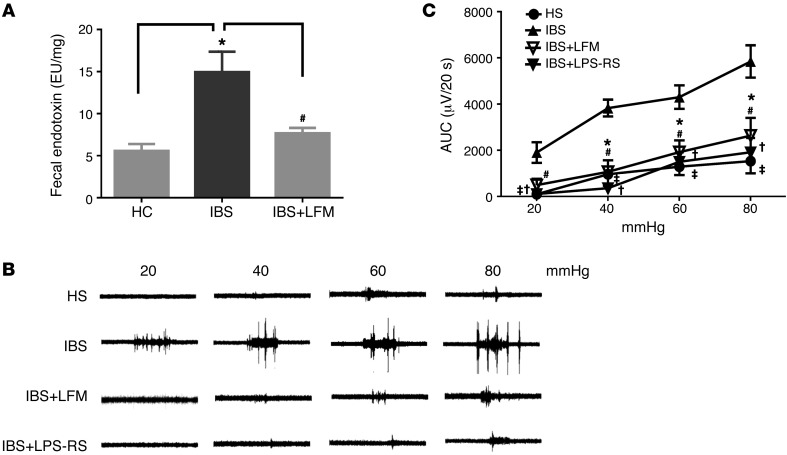
Figure 9. Effects of fecal supernatant from IBS-D patients on visceral sensitivity.
(A) Endotoxin level in fecal contents was elevated in IBS-D compared with HS (n = 6). (B) Representative electromyogram recordings of responses to colorectal distension showing that an intracolonic infusion of fecal supernatant from IBS-D patients induced visceral hyperalgesia in naive rats. This action was abolished by LPS-RS or treatment with low-FODMAP diet. (C) Bar chart showing that an intracolonic infusion of fecal supernatant from IBS-D patients induced visceral hyperalgesia in naive rats; this was prevented by LPS-RS or treatment with 4 weeks of low-FODMAP diet. Mean amplitudes of abdominal muscle contractions are expressed as area under the curve (AUC) after baseline subtraction (n = 5 per group). *P < 0.05 compared with HS; #P < 0.05 compared with IBS (IBS-D); ‡P < 0.05 and †P < 0.05 compared with IBS. HC, healthy controls; HS, healthy subjects; LFM, low-FODMAP diet; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; LPS-RS, LPS antagonist. P < 0.05, by 2-tailed Student’s t test or 2-way repeated-measures ANOVA.