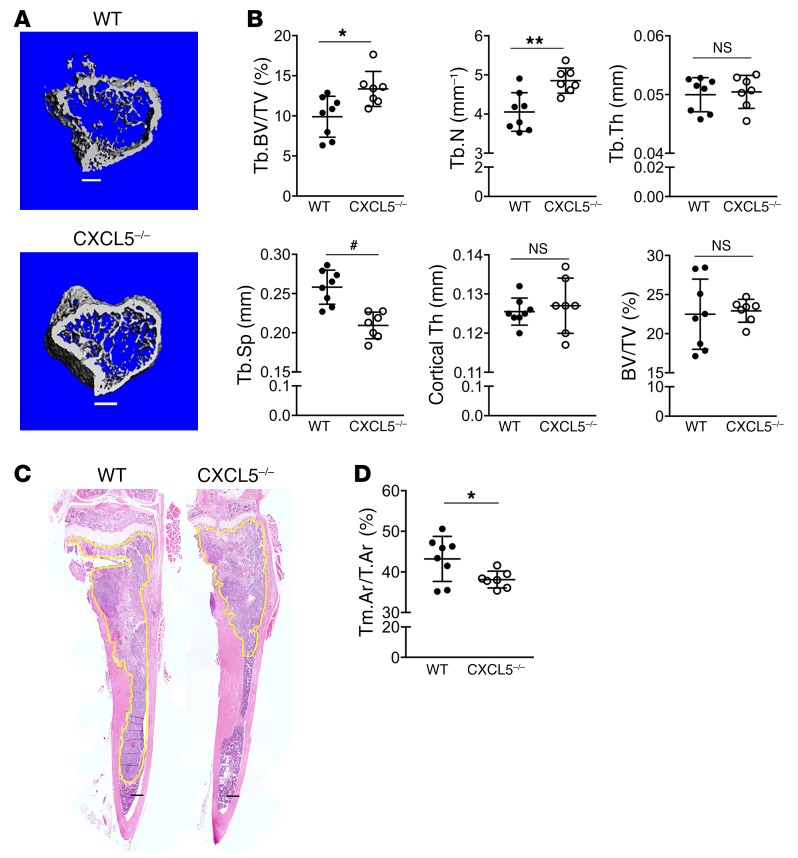
Figure 11. CXCL5 deficiency hinders tumor growth and bone osteolysis in the intratibial model.
Both WT (n = 8) and CXCL5–/– (n = 7) mice were inoculated with RM1-iC9 cells via intratibial injection and treated with AP, similarly to Figure 10A. (A) Representative μCT images showing trabecular bone in the tumor tibiae for WT and CXCL5–/– mice (scale bars: 400 μm). (B) Bone parameters were quantified by μCT in tumor-injected tibiae for WT and CXCL5–/–, similarly to Figure 10C. (C) Representative images of H&E sections for WT and CXCL5–/– tibiae. Tumors are highlighted in yellow (scale bars: 400 μm). (D) Quantification of tumor area relative to total bone area (Tm.Ar/T.Ar). Data are mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, #P < 0.001 (2-tailed Student’s t test).