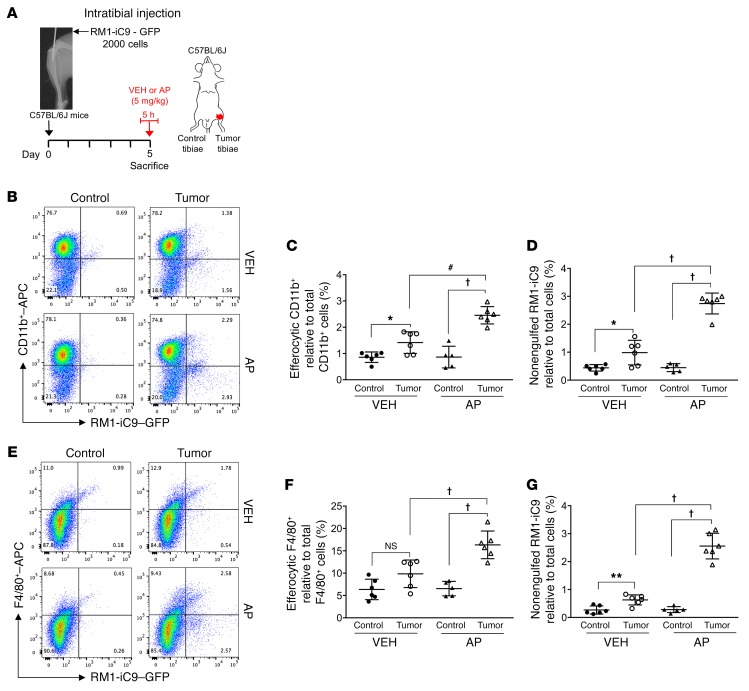
Figure 9. Engulfment of apoptosis-inducible RM1-iC9 cancer cells in the mouse model of intratibial inoculation.
(A) Experimental schematic. GFP-labeled RM1-iC9 cells (2 × 103) were inoculated in the left tibiae of C57BL/6J mice. Mice were randomized at day 5 (postinjection), divided into 2 groups, VEH- or AP-treated, for 5 hours, then sacrificed. Bone marrow cells were isolated and analyzed by flow cytometry using APC-labeled CD11b or F4/80 antibodies. (B) Representative flow cytometry plots corresponding to bone marrow cells isolated from tumor-inoculated and contralateral control tibiae stained with CD11b-APC antibody. (C) Percentage of CD11b+GFP+ (efferocytic) cells relative to total CD11b+ cells in the bone marrow population isolated for each tibia. (D) Percentage of nonengulfed GFP+ RM1-iC9 cancer cells relative to total bone marrow population for each tibia. (E–G) Corresponding plots and analyses similar to B–D, respectively, but using the F4/80-APC antibody; n = 6 mice per group with the exception of AP-Control (n = 5). Gates were established according to APC-labeled IgG isotype controls (see Supplemental Figure 6, A and B, for gating scheme). Data are mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, #P < 0.001, †P < 0.0001 (1-way ANOVA).