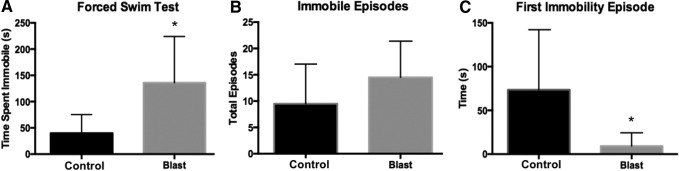
FIG. 5.
Blast exposure significantly increased depressive-like behavior (n = 6 per group). (A) Rats exposed to blast spent more time immobile compared with control rats (t = 2.49, p < 0.05). (B) No significant difference was seen on total number of immobility episodes. (C) The latency to first immobility episode was significantly shortened for the blast-exposed rats (t = 2.24, p < 0.05). *p < 0.05.