Figure 5. Influence of sex/estrous stage on protein expression of synaptic plasticity markers within the hippocampus (HPC) following treatment with vehicle or ketamine.
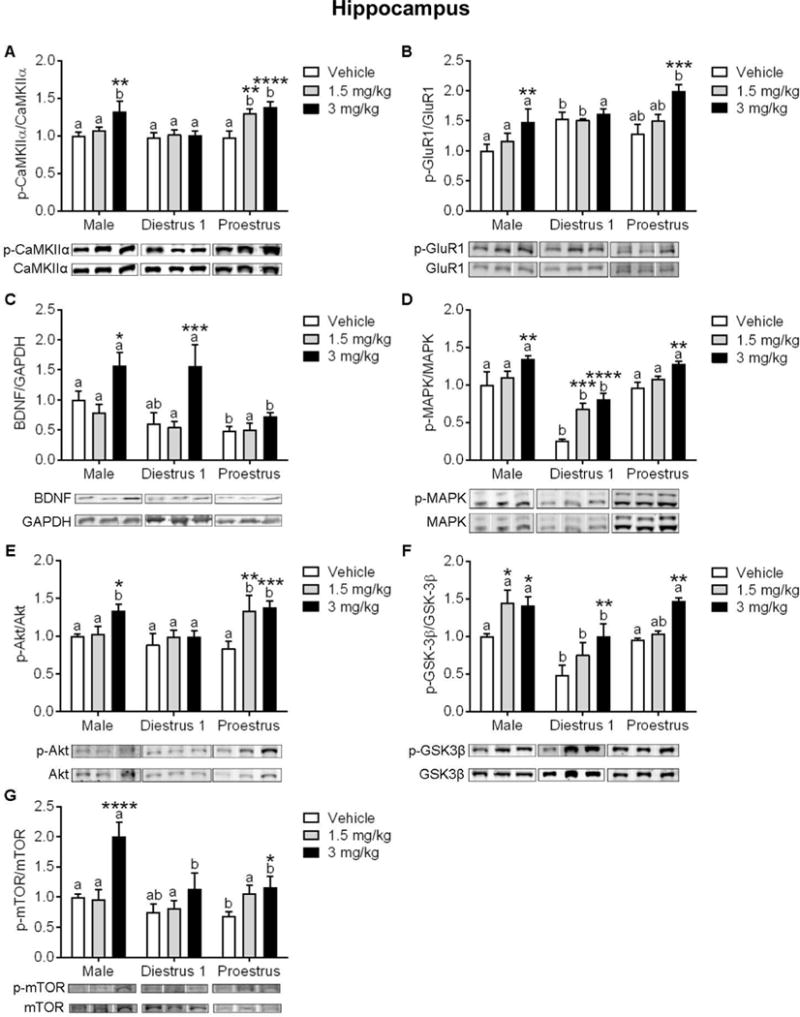
(A) Protein expression of p-CaMKIIα/CaMKIIα was increased by 1.5 mg/kg ketamine in Pro females, and in males and Pro females by 3 mg/kg. (B) Ketamine at 3 mg/kg increased expression of p-GluR1/GluR1 in males and Pro females, (C) and increased expression of BDNF in males and D1 females. (D) Protein expression of p-MAPK/MAPK was significantly lower in D1 females in all treatment conditions. Ketamine at 1.5 mg/kg increased expression of p-MAPK in D1 females, and in all groups at 3 mg/kg. (E) Ketamine at 1.5 mg/kg increased expression of p-Akt/Akt in Pro females, and 3 mg/kg increased expression in males and Pro females. (F) Ketamine at 1.5 mg/kg increased expression of p-GSK-3β/GSK-3β in males, and in all groups at 3 mg/kg. (G) Ketamine at 3 mg/kg increased p-mTOR/mTOR expression in males and D1 females. *p<.05, **p<.005, ***p<.0005, ****p<0.0001 vs. within-group vehicle. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences between sex/estrous stages within the vehicle treatment group. Data are means + SEM. (n=4–7/group)
